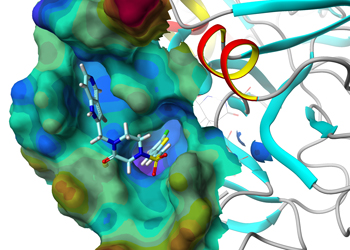
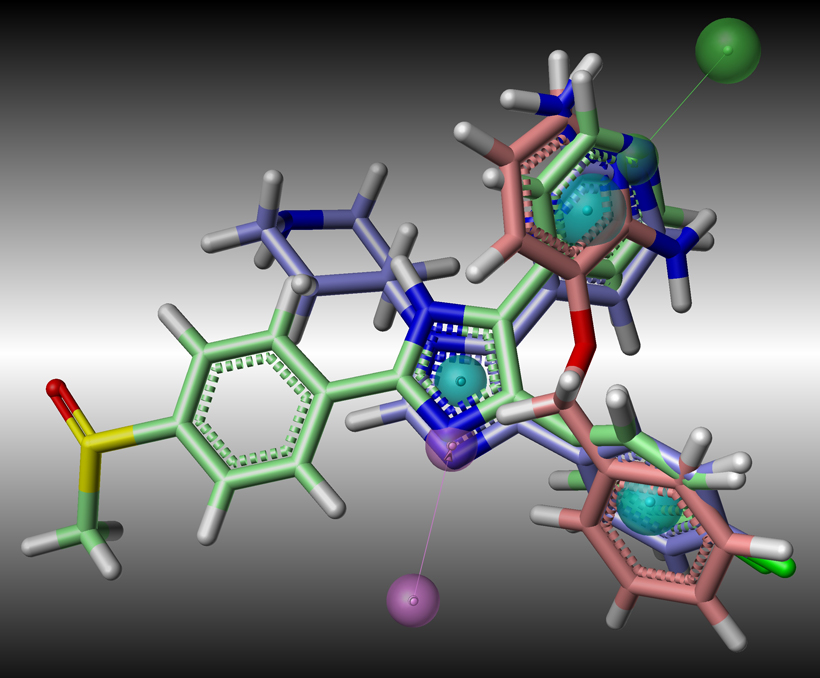
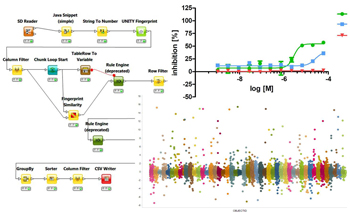
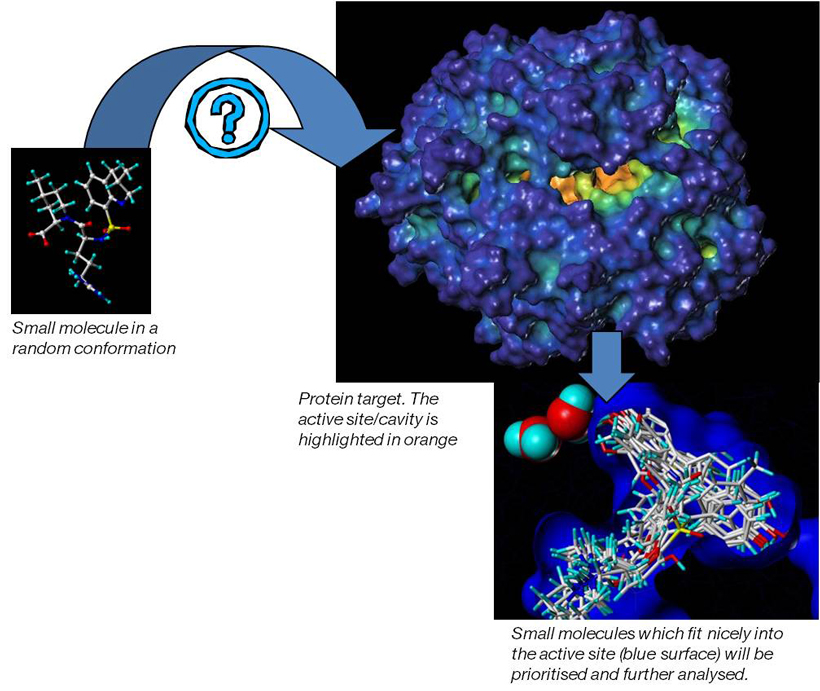
Computational chemistry methods are integral to the process of active molecule identification and optimisation. These include:
- Chemoinformatics approaches
- Molecular modelling
- Computational screening using ligand-based and structure-based design strategies
- Managing compound acquisition through our chemistry partners
- Commercial software available: SYBYL-X including SurflexDock and SurflexSim, LeadIT including FlexX and FlexS, Muse, Spartan
- Access to the HPC compute cluster at EMBL which provides access to more than 5800 CPUs for scientific computing at EMBL