10 January 2025

The Arendt Group at EMBL Heidelberg focuses on mechanisms of evolution, studying Platynereis dumerilli – evolutionarily ancient marine worms found broadly along European coasts.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
29 November 2024
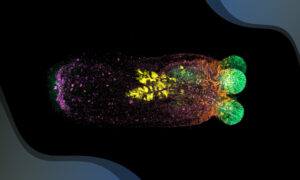
Scientists have shown how regenerating sea anemones restore their shape following a major injury, uncovering novel cellular and molecular mechanisms.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
25 January 2024
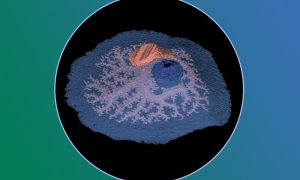
Sponges lack muscles and neurons. Yet, they make coordinated movements. Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg have discovered that sponge movement is controlled by an ancient ‘relaxant-inflammatory’ response that is also present in vertebrate blood vessels. The findings shed light on sponge physiology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
sciencescience-technology
5 November 2021

What can sponges tell us about the evolution of the brain? Sponges have the genes involved in neuronal function in higher animals. But if sponges don’t have brains, what is the role of these? EMBL scientists imaged the sponge digestive chamber to find out.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
5 October 2021

EMBL scientists and colleagues have developed an interactive atlas of the entire marine worm Platynereis dumerilii in its larval stage. The PlatyBrowser resource combines high-resolution gene expression data with volume electron microscopy images.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
3 June 2021

Under the innovative Planetary Biology research theme, EMBL scientists aim to understand life in the context of its environment.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
2 September 2010
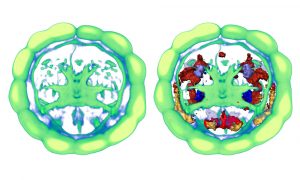
Our cerebral cortex, or pallium, is a big part of what makes us human: art, literature and science would not exist had this most fascinating part of our brain not emerged in some less intelligent ancestor in prehistoric times. But when did this occur and what were these ancestors? Unexpectedly,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
31 January 2010
The last ancestor we shared with worms, which roamed the seas around 600 million years ago, may already have had a sophisticated brain that released hormones into the blood and was connected to various sensory organs. The evidence comes not from a newly found fossil but from the study of microRNAs…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
No results found






