7 July 2023
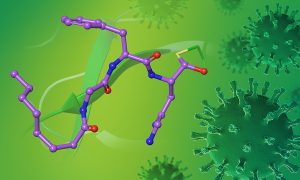
A collaboration between EMBL Grenoble and EBRIS scientists led to the characterisation of a new compound with promising activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
21 October 2021

The BY-COVID project aims to make infectious disease data, including COVID-19, openly available to everyone.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
14 October 2021

Largest in-depth analysis of genomic data tracks the spread of SARS-CoV-2 lineages in England.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
7 October 2021

EMBL will host a conference to look at the state of the pandemic, lessons learned, and ways to improve pandemic preparedness. Here’s a sneak peek into what promises to be another interesting and informative EMBL conference.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
eventsscience-technology
31 May 2021

The largest in-depth analysis of genomic surveillance data mapping out the dynamics of 62 lineages of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
17 May 2021
Leading international experts gathered to showcase progress in the fight against COVID-19 and share lessons for the future.
CONNECTIONS
29 April 2021

EMBL Hamburg’s integrated structural biology facility has contributed to the success of a large-scale SARS-CoV-2 study
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
9 April 2021

Researchers use large-scale human genetic studies to identify drug targets important for managing COVID-19 in its early stages
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
22 March 2021

EMBL alumnus Kai Simons did early work with Semliki Forest virus membranes, which is now central to a COVID-19 vaccine.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
alumniscience-technology
11 March 2021

EMBL alumnus Pawel Masiewicz has transferred skills and experience gained at EMBL to oversee starting materials for mRNA vaccine development.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
alumnipeople-perspectives
3 March 2021

EMBL invites Simon Gallow, an advocate at UN Women UK, to give a talk marking International Women’s Day.
LAB MATTERS
16 February 2021
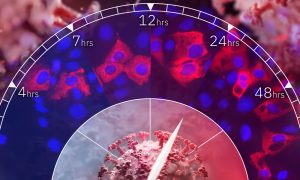
A team of EMBL scientists and colleagues have analysed how the novel coronavirus affects proteins in human cells. They identified several human proteins as potential drug targets to prevent viral replication.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
4 February 2021

Open letter galvanises life science community in support of open COVID-19 data
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2021
embl-announcementslab-matters
3 February 2021

A new lineage of coronavirus was first identified in the UK, but why is it spreading much more rapidly within the population?
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
20 January 2021

A note on the coronavirus variant B.1.1.7, which has first been described in the U.K. and has spread to 57 countries. The note summarises epidemiological information about the spread of B.1.1.7 in the U.K. collated and in part conducted by researchers from EMBL-EBI.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
5 January 2021

Understanding why disagreement is good for COVID science. EMBL Deputy Director General Ewan Birney offers tips for sorting through the discourse.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
people-perspectivesscience
21 December 2020

The story of a life-long friendship and a professional partnership that sowed the seeds for a ground-breaking vaccine technology.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
alumniscience-technology
17 December 2020

December has seen the start of a new chapter in the collaboration that has for years marked the relationship between the European Commission (EC) and EMBL.
CONNECTIONS
1 December 2020

Biotechnology company BioNTech and Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz conduct collaborative research with EMBL scientists at the beamline P12 in Hamburg
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
30 November 2020

Bioinformaticians at EMBL-EBI and beyond are adapting computational tools to investigate coronavirus genomes and proteins.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
23 November 2020
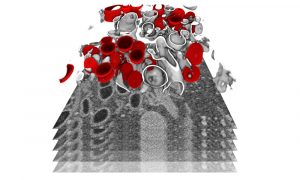
Researchers have studied SARS-CoV-2 replication in cells and obtained detailed insights into the alterations induced in infected cells. This information is essential to guide the development of urgently needed therapeutic strategies for suppressing viral replication and induced pathology.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
4 November 2020
By screening hundreds of sybodies (synthetic mini-antibodies), scientists have identified one that might stop SARS-CoV-2 from infecting human cells. This work, which holds promise for treating COVID-19, was conducted by EMBL Hamburg and collaborators from the Centre for Structural Systems Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
18 August 2020
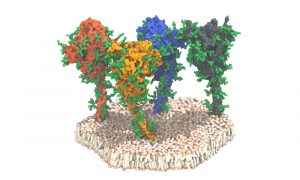
Researchers studied the spike protein on the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. With its spikes, the virus binds to human cells and infects them. The study gave surprising insights into the spike protein, including an unexpected freedom of movement and a protective coat to hide it from antibodies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
30 July 2020

Europe PMC has begun indexing full-text COVID-19 preprints along with the associated data. The project aims to accelerate research to fight the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
17 July 2020

European collaboration receives funding to explore risks and impact of future infectious disease outbreaks.
LAB MATTERS
8 July 2020
The virtual EMBL Conference ‘SARS-CoV-2: Towards a New Era in Infection Research’ explored the importance of fundamental research, collaboration, and data science in containing the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, and discussed opportunities to improve our response to pandemics in the future.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
eventsscience-technology
29 June 2020

To study how SARS-CoV-2 infects cells, the Gene Editing and Embryology Facility (GEEF) at EMBL Rome will generate mice that express a human version of a protein called ACE2. The mouse line will be shared with preclinical research collaborators carrying out vaccine and antibody trials, and with the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
29 June 2020
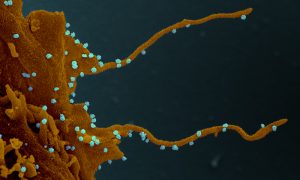
Researchers evaluate how the new coronavirus rewires human proteins for its own replication, and identify several antiviral drugs ready for clinical trials
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
25 June 2020

EMBL scientists develop a new molecular tool to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice. This tool is able to cause targeted epigenetic modifications of specific genes in specific cell populations. They will use it in mice to target airway cells that express the ACE2 protein – the receptor that…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
17 June 2020

While global research on coronaviruses has shed light on the function of many SARS-CoV-2 proteins, the role of some crucial components remains unknown. Researchers at EMBL Grenoble will use a range of structural biology methods to try to solve some of the puzzles of the molecular mechanics of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
16 June 2020

Scientists at EMBL and Heidelberg University Hospital are studying how the novel coronavirus behaves in the gut to try to better understand its epidemiology and prevent its spread. To do this, they are combining advanced imaging and sequencing technologies to study coronavirus in human intestinal…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
15 June 2020
The emergence of previously unknown pathogens, such as the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, raises many questions. To explore these questions in an international scientific forum, EMBL will host the virtual conference ‘SARS-CoV-2: Towards a New Era in Infection Research’ on 3 July. Invited…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2020
embl-announcementsevents
9 June 2020

EMBL researchers are studying COVID-19-related molecules by exposing them to high-brilliance X-ray beams. The Svergun group at EMBL Hamburg is using biological small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) as part of a global effort by scientists to elucidate the structural organisation of SARS-CoV-2…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
27 May 2020

EMBL and the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) restart the activities of the Joint Structural Biology Group in Grenoble to support coronavirus-related projects. A new initiative will allow users to be granted access to the High-Throughput Crystallisation (HTX) lab at EMBL and to a…
CONNECTIONS
26 May 2020

EMBL scientists have performed a large-scale analysis of over 4700 SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences. They found that many of the most interesting changes in the SARS-CoV-2 genome that have been reported so far are likely to be technical artefacts, rather than biological mutations.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
22 May 2020
Scientists hope that a legacy of the novel coronavirus in recovered COVID-19 patients – antibodies in their blood – could lead to drugs to treat others. The Merten group at EMBL Heidelberg has pivoted its microfluidics platform to support the search for neutralising antibodies that could…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
13 May 2020

EMBL scientists will contribute to the new German COVID-19 OMICS Initiative to study the biological mechanisms contributing to coronavirus infections. EMBL group leaders Jan Korbel and Oliver Stegle, who is also affiliated with the DKFZ Heidelberg, will coordinate the set-up of IT infrastructures…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
5 May 2020

By re-opening the High-Throughput Crystallisation (HTX) lab at EMBL Grenoble, EMBL is supporting structural biology projects to respond to the health threats posed by coronaviruses.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
30 April 2020

The Marquez Team has restarted operations at the High-Throughput Crystallisation (HTX) lab at EMBL Grenoble. The team has developed a fully automated protein-to-structure pipeline, which can be operated remotely and provides virtual access to the facilities.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
30 April 2020

EMBL electron microscopy specialists collaborate with researchers from Heidelberg University Hospital to understand the changes occurring in cell structures upon SARS-CoV-2 infection.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
28 April 2020

Scientists at EMBL Hamburg and Karolinska Institutet Stockholm aim to find synthetic antibodies – known as nanobodies – that bind a surface protein of the novel SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. Nanobodies could prevent the virus from entering human cells and causing COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
17 April 2020

EMBL Heidelberg reopens the Cryo-Electron Microscopy Service Platform to support coronavirus structural biology research.
CONNECTIONS
16 April 2020

Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg are contributing their expertise in a community effort to develop large-scale testing methods for coronavirus. Their goal is to increase the capacity and speed of testing, which is crucial for containing the pandemic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
15 April 2020

EMBL researchers are studying how drugs that have shown good results against COVID-19 work in living cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
15 April 2020

The Protein Expression and Purification Core Facility at EMBL Heidelberg will produce proteins for several coronavirus-related research projects, to assist the development of new strategies to fight the virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
No results found











































