
Working towards more responsible research assessment
Lab Matters A member of EMBL’s Responsible Research Assessment Working Group shares his thoughts on the importance of reforming strategies to assess research and researchers.
2024
lab-matters

Lab Matters A member of EMBL’s Responsible Research Assessment Working Group shares his thoughts on the importance of reforming strategies to assess research and researchers.
2024
lab-matters
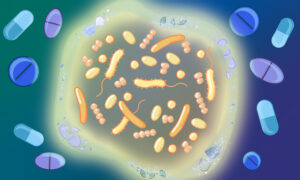
Science & Technology EMBL Heidelberg researchers compared the effect of drugs on isolated bacteria versus those growing in communities. This is the first study showing that bacteria are more resilient when in community due to cross-protection strategies. This could help researchers design more efficient therapies.
2024
science-technology

Lab MattersPeople & Perspectives The first EMBL-UNESCO infection biology research fellows share observations after residencies with EMBL researchers.
2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectivesperspectives
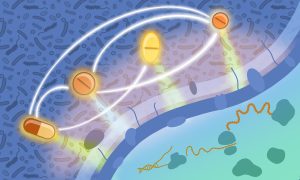
Science & Technology In an extensive investigation, EMBL researchers have tested over 10,000 drug combinations against some of the leading pathogenic bacteria carrying antimicrobial resistance and causing mortality.
2023
sciencescience-technology

Lab MattersScience & Technology To identify which drugs disrupt bacterial envelope integrity, the Typas group uses a molecule called chlorophenyl red-β-D-galactopyranoside.
2022
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology

Science & Technology EMBL researchers now understand the function of an elusive small DNA in bacteria and have developed a tool that can be used to better understand what might ‘switch on’ bacterial immune defences.
2022
sciencescience-technology

EMBL AnnouncementsLab Matters Cornelius Gross, Miki Ebisuya and Nassos Typas join EMBO, the prestigious organisation for the life sciences.
2022
embl-announcementslab-matters
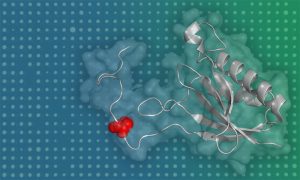
Science & Technology Researchers develop a new high-throughput approach to assess the functional significance of protein phosphosites.
2021
sciencescience-technology
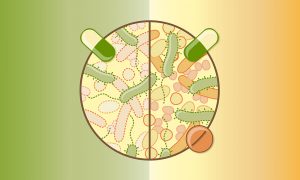
Science & Technology Researchers from EMBL’s Typas group and collaborators have analysed the effects of 144 antibiotics on the wellbeing of gut microbes. The study improves our understanding of antibiotics’ side effects and suggests a new approach to mitigating the adverse effects of antibiotics therapy on gut…
2021
sciencescience-technology
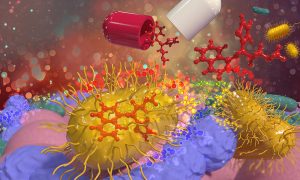
Science & Technology A new collaborative study led by EMBL group leaders Kiran Patil, Nassos Typas, and Peer Bork has found that common medications accumulate in human gut bacteria. This process reduces drug effectiveness and affects the metabolism of common gut microbes, thereby altering the gut microbiome.
2021
sciencescience-technology
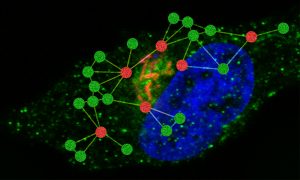
Science & Technology Research in the Typas group uncovers new details of the strategies Salmonella uses to survive in infected cells.
2021
sciencescience-technology
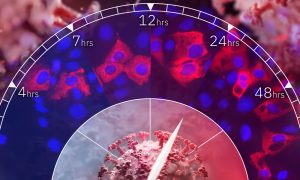
Science & Technology A team of EMBL scientists and colleagues have analysed how the novel coronavirus affects proteins in human cells. They identified several human proteins as potential drug targets to prevent viral replication.
2021
sciencescience-technology
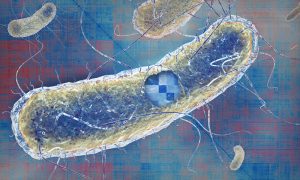
Science & Technology A new paper from EMBL’s Savitski team and Typas group describes their work on E. coli and how it brings a greater understanding of the way genes function and interact.
2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL AnnouncementsLab Matters Three changes in senior staff positions have been confirmed at EMBL today. Jessica Vamathevan becomes Head of Strategy, Jan Korbel becomes Head of Data Science for EMBL Heidelberg, and Nassos Typas becomes Senior Scientist.
2020
embl-announcementslab-matters
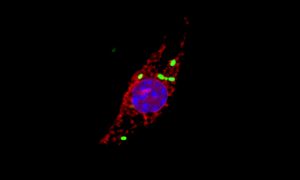
Science & Technology Scientists including members of EMBL’s Typas group have investigated how immune cells called macrophages respond to infection by the intracellular pathogen Salmonella enterica. They discovered that Salmonella causes newly produced cathepsins to accumulate in the nuclei of infected cells to…
2020
sciencescience-technology
Looking for past print editions of EMBLetc.? Browse our archive, going back 20 years.
EMBLetc. archive