
Celebrating 25 years of EMBL Rome
Lab Matters EMBL Rome celebrates its 25th anniversary this year – some impressions of the symposium and party organised for staff and alumni to mark this special occasion.
2024
lab-matters

Lab Matters EMBL Rome celebrates its 25th anniversary this year – some impressions of the symposium and party organised for staff and alumni to mark this special occasion.
2024
lab-matters

People & Perspectives Daniele Ancora is an ARISE fellow in the Light Imaging Facility at EMBL Rome. With a background in theoretical physics, he develops algorithms to improve image-based omics technologies. Learn about his interdisciplinary training and his little ‘obsessions’.
2024
people-perspectives

Connections At EMBL Rome, an immersive youth training programme is dedicated to, but also inspired by, alumnus Riccardo Cortese, thanks to private donors.
2024
connections

Science & Technology A study from the Hackett group at EMBL Rome led to the development of an epigenetic editing system that allows to precisely program chromatin modifications at any specific position in the genome, to understand their causal role in transcription regulation.
2024
science-technology
Science & Technology Scientists from EMBL Rome and EMBL Heidelberg found that disrupting the gut microbiome of male mice increases the risk of disease in their offspring. Their findings suggest that a father’s pre-conception environment can have lifelong effects on offspring.
2024
science-technology
Lab MattersPeople & Perspectives Diego Benusiglio, ETPOD postdoc in the Asari group at EMBL Rome, talks about his peculiar postdoctoral programme and his passion for science and Swing music
2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectives

Science & Technology A new study from the Asari group at EMBL Rome shows a different retinal function in awake mice compared to isolated retinal samples. These new insights could help to develop prosthetic devices that can act as a retina in the future.
2023
sciencescience-technology

Lab MattersPeople & Perspectives Gerald Pfister, Head of the Flow Cytometry Facility at EMBL Rome, talks about his private and professional passions and a return to his roots as part of the TREC project.
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives

Lab Matters EMBL Rome celebrated the European Researchers’ Night by participating in an event organised at the CNR Campus in Montelibretti.
2023
lab-matters

EMBL AnnouncementsLab Matters Interim head of EMBL Rome Cornelius Gross has been awarded an Advanced grant from the European Research Council (ERC) for his project TERRITORY, aimed at investigating the neural basis of territorial aggression and fear.
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters

ConnectionsLab Matters Scientists from EMBL and its French academic partners gathered at EMBL Rome for a workshop to foster collaboration and advance research in neuroscience.
2023
connectionslab-matters

Lab Matters 20 secondary school students from all over Italy participated in the fourth edition of Summer in Science at EMBL Rome.
2022
lab-matters

Science & Technology Recent studies from the Hackett group at EMBL Rome have revealed new insights on the mechanism regulating transmission of non-genetic information during embryonic development, and inspired a scientific illustration
2022
sciencescience-technology

Lab Matters After a two-year break, the summer school organised by Adamas Scienza and EMBL in collaboration with CNR is back. It will take place at the International Research Campus of Monterotondo (Rome) from 13 to 24 June 2022.
2022
lab-matters
Lab MattersScience & Technology Experiences at EMBL Rome led former group leader to establish his start-up in Italy, developing a new generation of gene therapies.
2022
alumnilab-mattersscience-technologytechnology-and-innovation

Science & Technology Researchers in the Gross group at EMBL Rome have investigated the mechanism behind defensive behaviour in mice. They have identified a specific area of the brain that encodes both spatial and threat cues to drive location-specific defensive responses.
2020
sciencescience-technology
Science & Technology An inherited mutation in a gene known as the guardian of the genome is likely the link between exploding chromosomes and some particularly aggressive types of cancer, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), the German Cancer Research Centre (DKFZ) and the University…
2012
sciencescience-technology
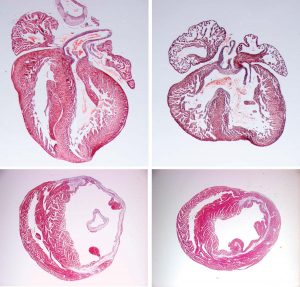
Science & Technology Almost a century after it was discovered in fruit flies with notches in their wings, the Notch signalling pathway may come to play an important role in the recovery from heart attacks. In a study published today in Circulation Research, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL)…
2009
sciencescience-technology
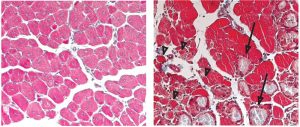
Science & Technology For scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy, what seemed like a disappointing result turned out to be an important discovery. Their findings, published online this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), provide…
2009
sciencescience-technology
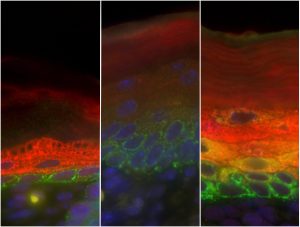
Science & Technology Stem cells have a unique ability: when they divide, they can either give rise to more stem cells, or to a variety of specialised cell types. In both mice and humans, a layer of cells at the base of the skin contains stem cells that can develop into the specialised cells in the layers above.…
2009
sciencescience-technology

Lab Matters Mice are one of biology’s most important model organisms, because 98% of their genes and many of their traits and diseases are similar to ours. Researchers at the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) take advantage of these similarities and use mice to study…
2009
lab-matters
Looking for past print editions of EMBLetc.? Browse our archive, going back 20 years.
EMBLetc. archive