EMBL-EBI leads International collaboration to share COVID-19 research data
EMBL-EBI set to launch European COVID-19 Data Platform to help store, share, and analyse research data linked to the COVID-19 pandemic.

EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and collaborators have started developing the European COVID-19 Data Platform, an initiative to help fight the SARS-CoV-2 virus by improving and accelerating the exchange of data among researchers globally.
A collaborative effort
The world is seeing an unprecedented number of research efforts to help combat the global COVID-19 pandemic. Understanding the biology, epidemiology, transmission, and evolution of the virus puts the scientific community one step closer to creating diagnostics, therapeutics, and effective vaccines. One of the greatest challenges at this stage is finding ways to rapidly access and share data and results.
The European COVID-19 Data Platform aims to address this challenge by providing an open, trusted, and scalable platform where researchers can store and share relevant datasets. It will also create a shared computational space where scientists and public health workers can collaborate. The data platform will be connected to the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC).
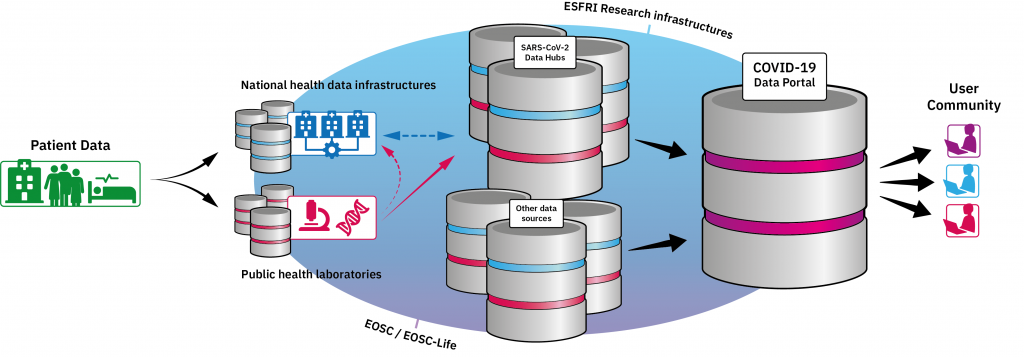
The European COVID-19 Data Platform consists of two connected components:
- SARS-CoV-2 Data Hubs, which will organise the flow of sequence data from the outbreak and provide comprehensive open data sharing for the European and global research communities.
- COVID–19 Data Portal, which will bring together and continuously update relevant COVID-19 datasets and tools.
Data Hubs
The SARS-CoV-2 Data Hubs will be built on EMBL-EBI infrastructure and will be used by public health agencies and scientists responsible for generating viral sequences at national or regional levels.
The sequence data in each Data Hub will differ to reflect national and regional efforts and requirements. Essential metadata will be captured, including sampling time, method, geographical location, sequencing technology, and the health status of the host. The Data Hubs will also provide systematic data processing, visualisation, and phylogenetic analysis tools.
EMBL-EBI will continue to work with existing collaborators on the creation and expansion of the Data Hubs model. These collaborators include the Erasmus Medical Centre in the Netherlands, the Technical University of Denmark and the Eötvös Loránd University in Hungary. EMBL-EBI will also establish new collaborations with other institutions to widen the scope of the initiative.
“Science, public health and healthcare have to work together if we want to minimise the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic,” says Marion Koopmans, Head of the Viroscience Department of the Erasmus Medical Centre in Rotterdam. “We are hoping that this initiative will enable researchers, clinicians and public health workers to safely and efficiently share their data in order to come up with answers to the most pressing questions about COVID-19.”
COVID-19 Data Portal
The first phase of the European COVID-19 Data Platform initiative is the launch of the COVID-19 Data Portal, which will feature relevant datasets from EMBL-EBI data resources such as the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA), UniProt, Protein Data Bank in Europe (PDBe), the Electron Microscopy Data Bank (EMDB), Expression Atlas, and Europe PMC. The portal will also include the outbreak sequence data and a Cohort Browser for searching clinical and epidemiological data. It will also enable scientists to upload, search, and explore specialist datasets.
In the coming weeks, additional datasets and tools from other European projects will be added, with the long-term objective of including data from other international projects. This will be achieved with the help of ELIXIR, the intergovernmental organisation that brings together life science data and resources from across Europe, and other collaborators.
“The COVID-19 Data Portal will be very easy for researchers to access and use,” says Guy Cochrane, Team Leader for Data Coordination and Archiving at EMBL-EBI. “Users will be able to upload their SARS-CoV-2 data and get access to data from other labs around the world. Analysis tools will also be available to help advance our collective knowledge of the virus.”
Getting involved
“We would like to encourage researchers working on the coronavirus outbreak to use the European COVID-19 Data Platform in their work,” says Rolf Apweiler, Director of EMBL-EBI. “Data sharing is key to understanding the spread of this virus and to the global effort to stop it spreading further.”
EMBL-EBI is hoping to collaborate with governments and organisations doing COVID-19 research who are interested in data sharing. Contact virus-dataflow@ebi.ac.uk if you are interested in getting involved.