First-ever blueprint of a minimal cell is more complex than expected
EMBL and CRG scientists reveal what a self-sufficient cell can’t do without
Click on image to download a high resolution image (tiff).
What are the bare essentials of life, the indispensable ingredients required to produce a cell that can survive on its own? Can we describe the molecular anatomy of a cell, and understand how an entire organism functions as a system? These are just some of the questions that scientists in a partnership between the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the Centre de Regulacio Genòmica (CRG) in Barcelona, Spain, set out to address. In three papers published back-to-back today in Science, they provide the first comprehensive picture of a minimal cell, based on an extensive quantitative study of the biology of the bacterium that causes atypical pneumonia, Mycoplasma pneumoniae. The study uncovers fascinating novelties relevant to bacterial biology and shows that even the simplest of cells is more complex than expected.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a small, single-cell bacterium that causes atypical pneumonia in humans. It is also one of the smallest prokaryotes – organisms whose cells have no nucleus – that don’t depend on a host’s cellular machinery to reproduce. This is why the six research groups which set out to characterize a minimal cell in a project headed by scientists Peer Bork, Anne-Claude Gavin and Luis Serrano chose M. pneumoniae as a model: it is complex enough to survive on its own, but small and, theoretically, simple enough to represent a minimal cell – and to enable a global analysis.
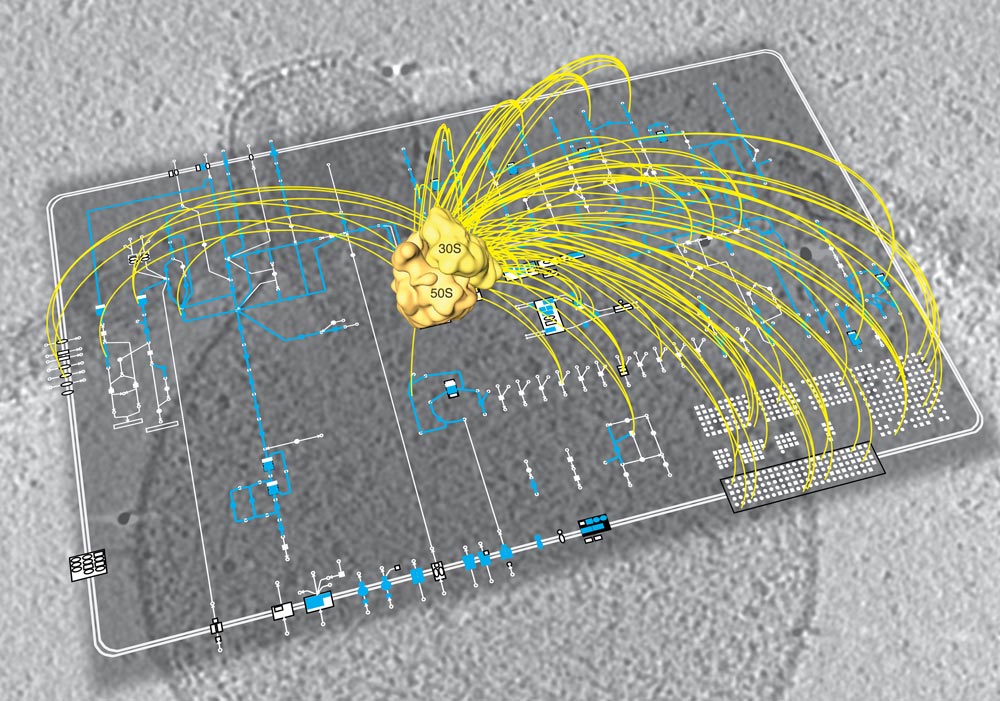
A network of research groups at EMBL’s Structural and Computational Biology Unit and CRG’s EMBL-CRG Systems Biology Partnership Unit approached the bacterium at three different levels. One team of scientists described M. pneumoniae’s transcriptome, identifying all the RNA molecules, or transcripts, produced from its DNA, under various environmental conditions. Another defined all the metabolic reactions that occurred in it, collectively known as its metabolome, under the same conditions. A third team identified every multi-protein complex the bacterium produced, thus characterising its proteome organisation. “At all three levels, we found M. pneumoniae was more complex than we expected”, says Luis , co-initiator of the project at EMBL and now head of the Systems Biology Department at CRG.
When studying both its proteome and its metabolome, the scientists found many molecules were multifunctional, with metabolic enzymes catalysing multiple reactions, and other proteins each taking part in more than one protein complex. They also found that M. pneumoniae couples biological processes in space and time, with the pieces of cellular machinery involved in two consecutive steps in a biological process often being assembled together.
Remarkably, the regulation of this bacterium’s transcriptome is much more similar to that of eukaryotes – organisms whose cells have a nucleus – than previously thought. As in eukaryotes, a large proportion of the transcripts produced from M. pneumoniae’s DNA are not translated into proteins. And although its genes are arranged in groups as is typical of bacteria, M. pneumoniae doesn’t always transcribe all the genes in a group together, but can selectively express or repress individual genes within each group.Unlike that of other, larger, bacteria, M. pneumoniae’s metabolism doesn’t appear to be geared towards multiplying as quickly as possible, perhaps because of its pathogenic lifestyle. Another surprise was the fact that, although it has a very small genome, this bacterium is incredibly flexible and readily adjusts its metabolism to drastic changes in environmental conditions. This adaptability and its underlying regulatory mechanisms mean M. pneumoniae has the potential to evolve quickly, and all the above are features it also shares with other, more evolved organisms.
“The key lies in these shared features”, explains Anne-Claude Gavin, an EMBL group leader who headed the study of the bacterium’s proteome: “Those are the things that not even the simplest organism can do without and that have remained untouched by millions of years of evolution – the bare essentials of life”.
This study required a wide range of expertise, to understand M. pneumoniae’s molecular organisation at such different scales and integrate all the resulting information into a comprehensive picture of how the whole organism functions as a system – an approach called systems biology.
“Within EMBL’s Structural and Computational Biology Unit we have a unique combination of methods, and we pooled them all together for this project”, says Peer Bork, joint head of the unit, co-initiator of the project, and responsible for the computational analysis. “In partnership with the CRG group we thus could build a complete overall picture based on detailed studies at very different levels.” Bork was recently awarded the Royal Society and Académie des Sciences Microsoft Award for the advancement of science using computational methods. Serrano was recently awarded a European Research Council Senior grant.