Gut microbes implicated in bladder cancer
Study shows that gut bacteria can metabolise carcinogens and cause them to accumulate in distant organs, leading to tumour development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
Showing results out of

Study shows that gut bacteria can metabolise carcinogens and cause them to accumulate in distant organs, leading to tumour development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

Jacqueline shares her experience of EMBL's international PhD programme.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2024
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
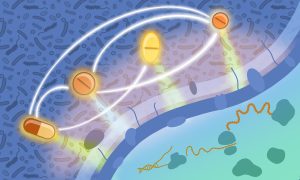
In an extensive investigation, EMBL researchers have tested over 10,000 drug combinations against some of the leading pathogenic bacteria carrying antimicrobial resistance and causing mortality.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

Ensembl 110 and Ensembl Genomes 57 have introduced in-house prokaryotic gene annotation across genomes available in Ensembl Bacteria. Since its inception, Ensembl Bacteria has imported user-submitted annotations from the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC) for…
2023
updates-from-data-resources

Enabling researchers worldwide to share and analyse pathogen data generated across the world
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation

Pascale Cossart, one of the world’s foremost authorities on the biology of Listeria, brings four decades of expertise in intracellular bacterial parasitism to EMBL as a visiting scientist.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
Researchers have identified hundreds of new bacterial species and viruses in the human skin microbiome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
A vast, curated collection of bacterial genomes is now organised, searchable and open to the community.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
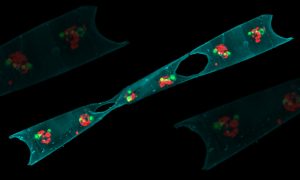
A technology around since the ‘60s, flow cytometry has increasing applications. New leadership at EMBL’s flow cytometry facilities is looking to ease use, expand training, and encourage more collaboration.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
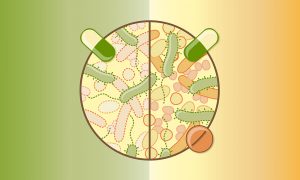
Researchers from EMBL’s Typas group and collaborators have analysed the effects of 144 antibiotics on the wellbeing of gut microbes. The study improves our understanding of antibiotics’ side effects and suggests a new approach to mitigating the adverse effects of antibiotics therapy on gut…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Structural biology provides insights into the diverse functions of fibrous protein in humans, amphibians, and bacteria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
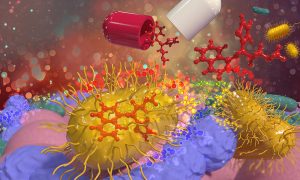
A new collaborative study led by EMBL group leaders Kiran Patil, Nassos Typas, and Peer Bork has found that common medications accumulate in human gut bacteria. This process reduces drug effectiveness and affects the metabolism of common gut microbes, thereby altering the gut microbiome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

After work in antimicrobial resistance, EMBL postdoc Laura Carroll is using machine learning for next-gen antibiotic development.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2021
people-perspectivesscience

EMBL group leaders Julia Mahamid, Anna Kreshuk & Jonas Ries awarded Chan Zuckerberg Initiative grant to advance what we see inside cells.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives

Gautam Dey is fascinated by the evolutionary origins of the nucleus, and is looking forward to making the most of EMBL's infrastructure.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives

Freshwater sports can cause waterborne infections, but real-time DNA sequencing could help.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Researchers at the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology and EMBL Hamburg, in collaboration with scientists in Israel and Spain, have discovered remarkable molecular properties of an antimicrobial peptide from the skin of the Australian toadlet. The discovery could inspire the development of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

To study the effect of commonly used drugs on bacterial envelopes, EMBL scientists applied a biochemical assay using a colour reaction. The deeper the red, the stronger the disruptive effect of the drug.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

EMBL Hamburg and Tara raise awareness of the risks of microplastic pollution and global infection
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2019
embl-announcementsevents

Colorectal cancer characterised by consistent changes in gut bacteria across continents, cultures and diets
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

Scientists honoured for contributions in cancer immunotherapy and structural biology
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2019
alumnipeople-perspectives
Suicide system in tuberculosis bacteria might hold key to treatment
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
New search engine allows researchers to identify antibiotic resistance genes or mutations in real time
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
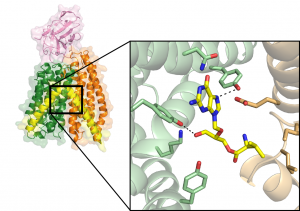
Scientists develop structural model that could help in the development of drugs with increased absorption rates
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

EMBL’s GeneCore steps up to discover the facts and settle disputes
LAB MATTERS2018
lab-matters

Meet the organisers of EMBO’s first course on molecular geobiology
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
eventsscience-technology
First global survey of soil genomics reveals a war between fungi and bacteria
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Scientists show how bacteria and other microorganisms are passed on from mother to child
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists investigate how bacteria melt to study their reaction to drugs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Combining antibiotics with each other, non-antibiotic drugs or food additives can alter their effectiveness
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Dog and human gut microbiomes have more similar genes and responses to diet than previously thought
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2018
people-perspectivesscience
One in four drugs with human targets inhibit the growth of bacteria in the human gut, and may promote antibiotic resistance, EMBL researchers report in Nature
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists show how to grow a wide range of gut bacteria in the lab
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
In a nutshell : The gut metagenome is the collection of all the genomes of all the microbes in the human intestinal tract : it is specific to each human, like a second genetic signature At least in healthy humans, this personal metagenome is stable over time The gut metagenome is…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
The bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae, which causes atypical pneumonia, is helping scientists uncover how cells make the most of limited resources. By measuring all the proteins this bacterium produces, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
In the future, when you walk into a doctor’s surgery or hospital, you could be asked not just about your allergies and blood group, but also about your gut type. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and collaborators in the international MetaHIT…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
The thousands of bacteria, fungi and other microbes that live in our gut are essential contributors to our good health. They break down toxins, manufacture some vitamins and essential amino acids, and form a barrier against invaders. A study published today in Nature shows that, at 3.3 million,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
The last ancestor we shared with worms, which roamed the seas around 600 million years ago, may already have had a sophisticated brain that released hormones into the blood and was connected to various sensory organs. The evidence comes not from a newly found fossil but from the study of microRNAs…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
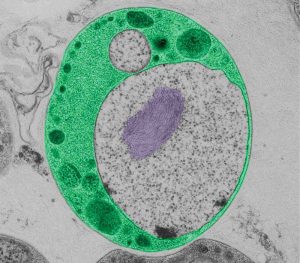
Although they are present almost everywhere, on land and sea, a group of related bacteria in the superphylum Planctomycetes-Verrucomicrobia-Chlamydiae, or PVC, have remained in relative obscurity ever since they were first described about a decade ago. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
In 1870 the German scientist Ernst Haeckel mapped the evolutionary relationships of plants and animals in the first ‘tree of life’. Since then scientists have continuously redrawn and expanded the tree adding microorganisms and using modern molecular data, yet, many parts of the tree…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
No results found