7 July 2025
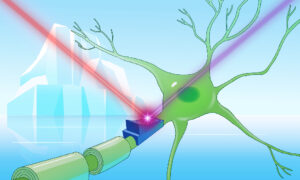
‘Cryorhodopsins’ are a group of unusual and colourful microbial molecules found exclusively in cold environments. Some of them are blue, a rare and sought-after light-absorption property. They are the first observed molecules that can act as both ‘on’ and ‘off’ switches for electrical…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
19 December 2023

EMBL Hamburg, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Postnova Analytics GmbH, and BioNTech SE have developed a new method to quantitatively investigate sizes of nanoparticles containing mRNA. It may become an important part of regular characterisation of mRNA nanomedicines in the future.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
14 December 2023

EMBL Hamburg is located at the PETRA III synchrotron, which in the future, will be upgraded to PETRA IV. Selina Storm is theEMBL@PETRA IV Programme Manager. Here, she speaks about her role and the benefits of PETRA IV for EMBL.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
2 October 2023

Pioneers of the mRNA nanomedicines technology receive 2023 Nobel Prize in Physiology or medicine. EMBL is pleased to have supported the development of the application of the mRNA nanomedicine technology through our long-standing collaboration with BioNTech, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
6 September 2023
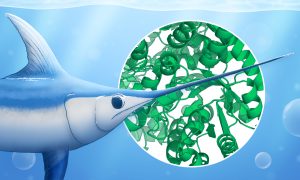
Learn how scientists use bio-SAXS, an experimental X-ray technique, to study the shape and dynamics of proteins and other biomolecules. SAXS can be even used to analyse the structure of mineral particles in the swordfish sword bone, which can help scientists better understand bone ageing.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
8 August 2023

Clément Blanchet has been appointed to lead the team working on small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) at EMBL Hamburg. In this interview, he talks his ambitions for the future work of the SAXS Team, his passion for science, and a memorable ‘aha’ moment he had in his early career.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
15 May 2023

EMBL Grenoble technology teams provide a sneak peek into their latest collaborative project in structural biology services: the complete automation of an integral step in X-ray crystallography.
EMBLetc
17 March 2023

Biological X-ray imaging is an emerging technology that uses X-rays to image tissues or even entire organisms. It will play an important role in EMBL Hamburg’s future service portfolio, and will allow studying life on multiple scales. Team Leader Liz Duke discusses her plans to establish X-ray…
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
1 March 2023

Physicists, engineers and robotics experts work together in EMBL Hamburg’s Instrumentation Team to design instruments that support structural biology research. The team has finished a transfer robot that facilitates automated handling of protein crystals with care and precision. This will help…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
lab-mattersscience-technology
1 December 2022
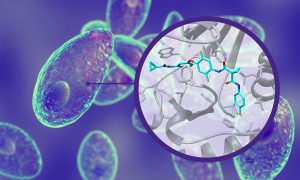
Recent studies supported by EMBL Grenoble’s expertise in structural biology research and scientific services have identified Altiratinib as a potential drug to stop toxoplasmosis infection and opened up treatment options against malaria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
16 November 2022

Kirill Kovalev, an EMBL Hamburg researcher, is studying the structure of an ancient bacterial molecule to help scientists control brain cell activity
EMBLetc
3 November 2022

Researchers and engineers have integrated a CrystalDirect harvester into the fully automated beamline MASSIF-1, a unique combination of structural biology technologies that is now open to external academic users.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
lab-mattersscience-technology
8 June 2022

Two former EMBL staff members have been recognised for their outstanding contributions to research in the fields of brain evolution and cancer.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2022
alumniembl-announcements
7 December 2021
RNA vaccines, such as the ones for COVID-19, represent a new approach in vaccine technology. Cy Jeffries, faculty staff scientist at EMBL Hamburg, explains the clever technology behind RNA vaccines, and how structural biology contributes to its development. EMBL Hamburg collaborated on several…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
5 November 2021

Ken Holmes, outstanding pioneer of structural biology and founder of EMBL´s Hamburg site, died on 2 November 2021 at the age of 87.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
alumnipeople-perspectives
15 October 2021
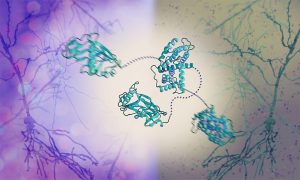
The Graham and Crump groups at the University of Cambridge and the Svergun Group at EMBL Hamburg have discovered a mechanism by which the herpes simplex virus takes control of the molecular machinery of human cells. Their work reveals how a dedicated viral protein hijacks key host proteins, forcing…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
10 August 2021

MASSIF-1, run jointly by EMBL Grenoble and the ESRF, is a beamline for macromolecular crystallography. It is used by the research community to study the 3D structure of proteins, which is important for drug development.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
13 July 2021

EMBL alumni Ilaria Piazza and Ken Holmes have been recognised for their outstanding contributions, and will receive their awards as part of the celebrations for EMBL World Alumni Day.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2021
alumnipeople-perspectives
29 April 2021

EMBL Hamburg’s integrated structural biology facility has contributed to the success of a large-scale SARS-CoV-2 study
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
6 April 2021
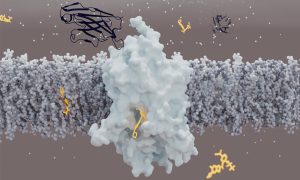
Scientists have determined the structure of Glycine Transporter 1. The finding could open new avenues for developing therapeutics for psychiatric disorders
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
26 January 2021

Engineers at EMBL Hamburg installed specially designed mirrors to reflect and focus X-ray beams onto tiny crystals made of proteins or other biological molecules.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
1 December 2020

Biotechnology company BioNTech and Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz conduct collaborative research with EMBL scientists at the beamline P12 in Hamburg
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
25 August 2020

The beamlines run jointly by EMBL Grenoble and the ESRF reopen today, unveiling significant upgrades that exploit the brand new fourth generation ESRF synchrotron source.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2020
embl-announcementsscience
9 June 2020

EMBL researchers are studying COVID-19-related molecules by exposing them to high-brilliance X-ray beams. The Svergun group at EMBL Hamburg is using biological small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) as part of a global effort by scientists to elucidate the structural organisation of SARS-CoV-2…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
27 May 2020

EMBL and the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) restart the activities of the Joint Structural Biology Group in Grenoble to support coronavirus-related projects. A new initiative will allow users to be granted access to the High-Throughput Crystallisation (HTX) lab at EMBL and to a…
CONNECTIONS
28 April 2020

Scientists at EMBL Hamburg and Karolinska Institutet Stockholm aim to find synthetic antibodies – known as nanobodies – that bind a surface protein of the novel SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. Nanobodies could prevent the virus from entering human cells and causing COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
17 September 2019
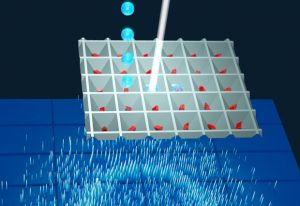
Researchers from Hamburg simplify time-resolved X-ray crystallography
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
31 October 2018

Speeding up time-resolved X-ray crystallography with EMBL beamline P14
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
21 April 2016

Florent Cipriani talks about his passion for developing beamline instrumentation
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
22 September 2015

MASSIF-1 processes its 10,000th crystal, less than one year after the beamline became operational.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
28 November 2014

In two months, 2.3 million diffraction images collected on new, fully automated ESRF/EMBL beamline.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
8 November 2009
Much as adrenaline coursing through our veins drives our body’s reactions to stress, the plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) is behind plants’ responses to stressful situations such as drought, but how it does so has been a mystery for years. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
1 February 2007

The German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF) has awarded 8.8 Million Euro to the Hamburg Outstation of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) for the construction of an Integrated Research Facility for Structural Biology at the new PETRA-III storage ring of the German…
LAB MATTERS
No results found































