
Changes in EMBL leadership
Peer Bork and Ewan Birney take up interim leadership of EMBL as Edith Heard steps down as Director General.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2025
embl-announcements
Showing results out of

Peer Bork and Ewan Birney take up interim leadership of EMBL as Edith Heard steps down as Director General.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2025
embl-announcements

EMBL announces that Peer Bork and Ewan Birney will lead the organisation after the departure of Director General Edith Heard in summer 2025.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2024
embl-announcements
Scientists have developed a new machine-learning model to predict microbial load — the density of microbes in our guts — and used it to demonstrate how microbial load plays an important role in disease-microbiome associations.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
EMBL Heidelberg researchers compared the effect of drugs on isolated bacteria versus those growing in communities. This is the first study showing that bacteria are more resilient when in community due to cross-protection strategies. This could help researchers design more efficient therapies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

EMBL’s planetary biology flagship TREC expedition has officially started. The new project applies EMBL's expertise and technologies in molecular and cellular biology to current environmental challenges, and connects with a wide range of research disciplines.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2023
embl-announcementseventsscience

EMBL is leading the TREC project: the first pan-European and cross-disciplinary effort to examine life in its natural context.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
New research by EMBL scientists shows at atomic detail how antibiotics affect the process of protein production inside bacteria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

EMBL researchers used data from over 300 human faecal microbiota transplants to gain an ecological understanding of what happens when two gut microbiomes clash.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

Bork Group at EMBL Heidelberg analysed a new global gene database to study how genes emerge and spread across various habitats on our planet. In the future, the group will expand the database and use it for studying microbial gene evolution and dispersal at a finer-grained scale.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Researchers studying a massive cohort of European patients have found that commonly prescribed drugs for cardiometabolic disorders can have long-term effects on the gut microbiome. Such effects can complicate the understanding of how disease affects the microbiome and must be taken into…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
A new collaborative study led by EMBL group leaders Kiran Patil, Nassos Typas, and Peer Bork has found that common medications accumulate in human gut bacteria. This process reduces drug effectiveness and affects the metabolism of common gut microbes, thereby altering the gut microbiome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Distinctions recognise Peer’s development and sharing of bioinformatics tools as well as his significant contributions to bioinformatics research, education, and services.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives

Researchers investigate how external factors can influence the persistence of microbe species in the human gut
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Under the innovative Planetary Biology research theme, EMBL scientists aim to understand life in the context of its environment.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists have discovered that the proteome is substantially affected by both sex and diet
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
Many microbes traverse the oral-gut barrier
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
First global survey of soil genomics reveals a war between fungi and bacteria
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Scientists show how bacteria and other microorganisms are passed on from mother to child
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Dog and human gut microbiomes have more similar genes and responses to diet than previously thought
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2018
people-perspectivesscience
One in four drugs with human targets inhibit the growth of bacteria in the human gut, and may promote antibiotic resistance, EMBL researchers report in Nature
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists show how to grow a wide range of gut bacteria in the lab
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Participants learn about EMBL’s ocean biodiversity research at the Fall Gala
CONNECTIONS2016
connectionsevents

EMBL scientists regularly receive prestigious awards – meet the latest honourees.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2016
embl-announcementslab-matters

27 former Bork lab members joined Peer for a full-day get-together this summer
LAB MATTERS2016
alumnilab-matters
Stool transplants: finding the right match important, EMBL study shows
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Collaboration between scientists reveals collaboration between lipids.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
A fungus that lives at extremely high temperatures could help understand structures within our own cells. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and Heidelberg University, both in Heidelberg, Germany, were the first to sequence and analyse the genome of a heat-loving fungus,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
In the future, when you walk into a doctor’s surgery or hospital, you could be asked not just about your allergies and blood group, but also about your gut type. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and collaborators in the international MetaHIT…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
The thousands of bacteria, fungi and other microbes that live in our gut are essential contributors to our good health. They break down toxins, manufacture some vitamins and essential amino acids, and form a barrier against invaders. A study published today in Nature shows that, at 3.3 million,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
The last ancestor we shared with worms, which roamed the seas around 600 million years ago, may already have had a sophisticated brain that released hormones into the blood and was connected to various sensory organs. The evidence comes not from a newly found fossil but from the study of microRNAs…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
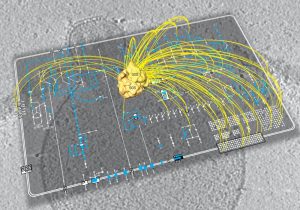
What are the bare essentials of life, the indispensable ingredients required to produce a cell that can survive on its own? Can we describe the molecular anatomy of a cell, and understand how an entire organism functions as a system? These are just some of the questions that scientists in a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
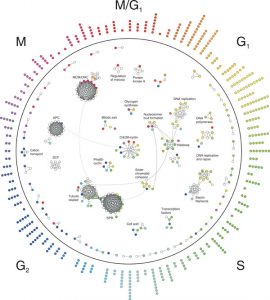
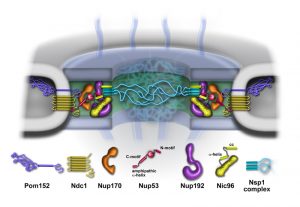
Most things that happen in the cell are the work of ‘molecular machines’ – complexes of proteins that carry out important cellular functions. Until now, scientists didn’t have a clear idea of when proteins form these machines – are these complexes pre-fabricated or put…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
No results found