21 August 2024
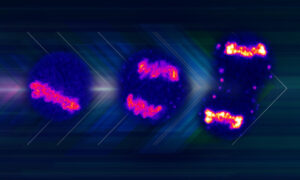
EMBL Heidelberg researchers discovered how a protein switches between repelling and gluing chromosomes during cell division. This helps the mother cell to divide the genome equally into two daughter cells and cluster chromosomes inside the daughter nuclei, ensuring a successful cell division.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
8 August 2024

EMBL-Stanford Life Science Alliance fellow Jana Helsen shares how she balanced her life between two laboratories and countries, her latest research paper, and her passion for cover art.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
22 May 2024

New research by EMBL scientists shows how different modes of cell division used by animals and fungi might have evolved to support diverse life cycles.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
23 November 2023

Alba Diz-Muñoz and Arnaud Krebs from EMBL Heidelberg have received grants to work on projects that aim, respectively, to understand the cellular mechanics that control cell division and investigate the regulatory networks that govern transcription factor function.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
21 November 2019
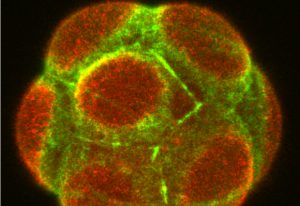
Shedding light on the mechanisms that control the fate of embryonic cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
2 July 2019
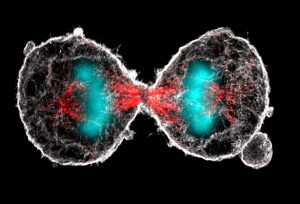
What looks like a pair of scary alien eyes is actually the final stage in the duplication of a cell. Cell duplication is preceded by a process called mitosis, in which the replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Mitosis is the prerequisite for a cell to divide into two identical…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
31 January 2019

A collection of the most read articles from the EMBL news website in 2018
LAB MATTERS
10 September 2018
Real-time tracking of proteins during mitosis is now possible using a 4D computer model
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
12 July 2018
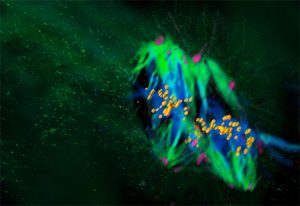
Mammalian life begins differently than we thought
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
7 December 2016

Paul Nurse’s failed experiment inspired a career that would uncover key mechanisms of cell division
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
21 March 2016
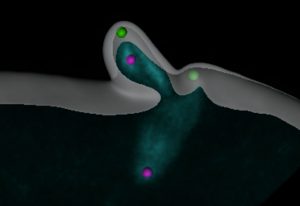
1st real-time video of starfish egg cell eliminating crucial structures, to ensure embryo viability
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
7 March 2016
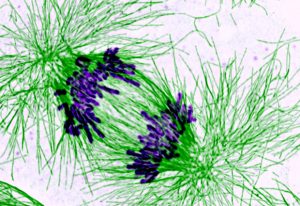
Structural insights into how cohesin keeps DNA together during the cell cycle
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
18 May 2014
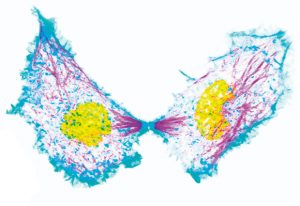
DNA-coralling protein complex in an unexpected bind
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
18 August 2011
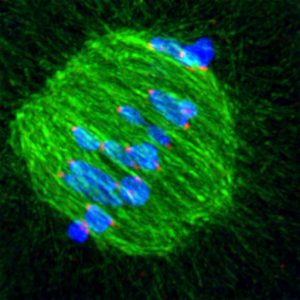
When an egg cell is being formed, the cellular machinery which separates chromosomes is extremely imprecise at fishing them out of the cell’s interior, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have discovered. The unexpected degree of trial-and-error…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
17 June 2011
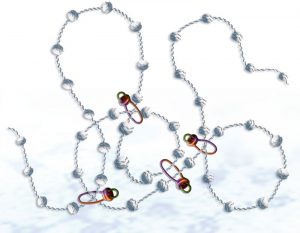
As any rock-climber knows, trailing a long length of rope behind you is not easy. A dangling length of rope is unwieldy and hard to manoeuvre, and can get tangled up or stuck on an outcropping. Cells face the same problem when dragging chromosomes apart during cell division. The chromosomes are…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
5 August 2010
During cell division, microtubules emanating from each of the spindle poles meet and overlap in the spindle’s midzone. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have uncovered the molecular mechanism that determines the extent of this overlap. In a…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
1 April 2010
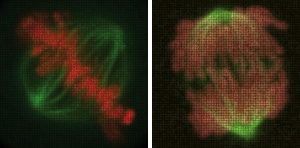
Name a human gene, and you’ll find a movie online showing you what happens to cells when it is switched off. This is the resource that researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and their collaborators in the Mitocheck consortium are making freely…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
3 December 2008
Cell division is one of the most fundamental processes of life. It explains how one cell can give rise to an organism of several million cells, it determines the shape of different life forms and it underpins our body’s capacity to heal when injured. Often we only notice how important cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
10 June 2007
A human cell contains an enormous 1.8 metres of DNA partitioned into 46 chromosomes. These have to be copied and distributed equally into two daughter cells at every division. Condensation, the shortening of chromosomes, allows the cell to handle such huge amounts of genetic material during cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
4 May 2007
When a cell divides, normally the result is two identical daughter cells. In some cases however, cell division leads to two cells with different properties. This is called asymmetric cell division and plays an important role in embryonic development and the self-renewal of stem cells. Researchers…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
25 August 2006
Cells in an embryo divide at an amazing rate to build a whole body, but this growth needs to be controlled. Otherwise the result may be defects in embryonic development or cancer in adults. Controlling growth requires that some cells divide while others die; their fates are determined by signals…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
31 October 2005
The Commission of the European Union has awarded EUR 9 million over five years for a new Network of Excellence that will make computational systems biology accessible to bench scientists throughout Europe and beyond. ENFIN, which stands for ‘Experimental Network for Functional…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
lab-mattersscience-technology
4 September 2005
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and the Institute of Biomedical Research of the Parc Científic de Barcelona (IRB-PCB) have now added key evidence to claims that some types of cancer originate with defects in stem cells. The study, reported this week in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
13 July 2005
Microtubules need a helping hand to find chromosomes in dividing egg cells, scientists have discovered. Although it was generally accepted that microtubules act alone as the cellular ropes to pull chromosomes into place, a new study by researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL)…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
12 July 2005

A systematic search through human genes has begun at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany. Working within the MitoCheck consortium that includes 10 other institutes throughout Europe, the EMBL scientists will silence all human genes, one-by-one, to find those…
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS
2005
connectionslab-matters
No results found
















