
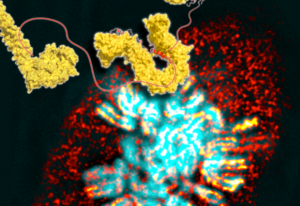
MAGIC: AI-assisted laser tag illuminates cancer origins
EMBL researchers have developed a new AI tool, which, through a game of molecular laser tag, is helping us better understand the origins of cancer.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
Showing results out of

EMBL researchers have developed a new AI tool, which, through a game of molecular laser tag, is helping us better understand the origins of cancer.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
EMBL scientists have shown how overlapping loops of DNA stack upon each other in dividing cells to give rise to rod-shaped chromosomes.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
EMBL Heidelberg researchers discovered how a protein switches between repelling and gluing chromosomes during cell division. This helps the mother cell to divide the genome equally into two daughter cells and cluster chromosomes inside the daughter nuclei, ensuring a successful cell division.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

EMBL-Stanford Life Science Alliance fellow Jana Helsen shares how she balanced her life between two laboratories and countries, her latest research paper, and her passion for cover art.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2024
people-perspectives
Researchers have discovered the mechanism by which a family of DNA motor proteins packages loosely arranged strands of DNA into compact individual chromosomes during cell division.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
Researchers have uncovered how cells remove unwanted components from the nucleus following mitosis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
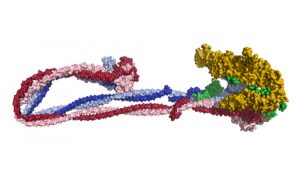
EMBL scientists and collaborators help reveal the process by which enormous quantities of DNA are folded into cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
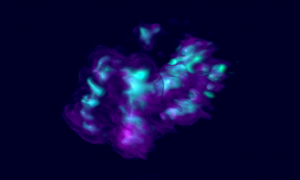
In human cells, the genetic material is packaged into 23 different DNA molecules, the chromosomes. Each chromosome is present in two copies, one inherited from the paternal sperm, and the other from the maternal egg. During most of the cell’s life, chromosomes take the shape of long,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
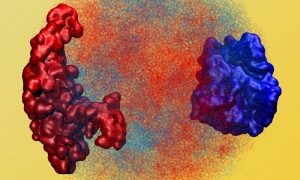
EMBL researchers in the Heard group at EMBL Heidelberg explore the interaction between DNA organisation and gene expression in the early embryo
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Researchers at Harvard Medical School and EMBL-EBI have carried out the largest analysis across cancer types of the newly discovered mutational phenomenon chromothripsis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
DNA is present in each cell of our body. If all the DNA from one human cell was removed and aligned in a single strand, it would in theory add up to a total length of about two metres. In order to fit into the nucleus of a cell, DNA has to be compressed by […]
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
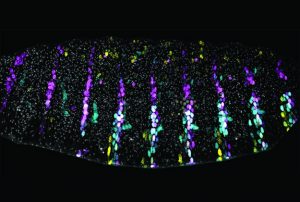
Enhancers in Drosophila embryos gather together to preserve phenotypes under stressful conditions
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

Does rearranging chromosomes affect their function? EMBL scientists reveal uncoupling of 3D chromatin organisation and gene expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
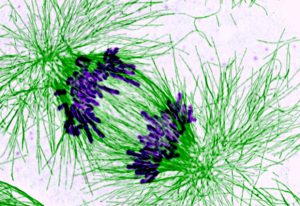
The mystery of how condensin maintains the integrity of the genome during cell division.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

A collection of the most read articles from the EMBL news website in 2018
LAB MATTERS2019
lab-matters
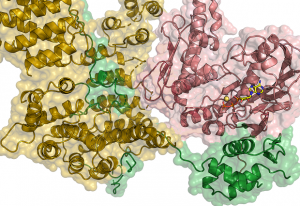
EMBL scientists discover how a component of the cohesin ring binds DNA
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Which of our genes will be passed on to our children? Simone Köhler wants to find out
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2018
people-perspectivesscience
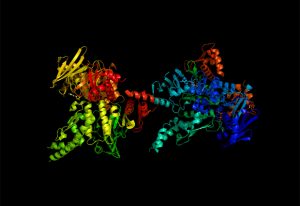
EMBL’s next Director General reflects on the questions that drive her research
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2018
people-perspectivesscience

EMBL alumna Melina Schuh recognised for excellence in science
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2018
alumnipeople-perspectives
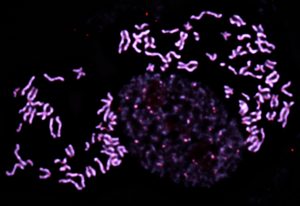
EMBL group leader Jan Korbel reflects on his scientific origins and current research
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
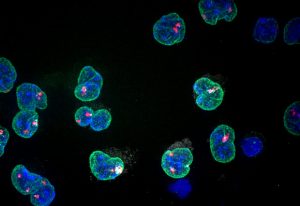
EMBL scientists count and locate chromosomal proteins during cell duplication
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

New EMBL group leader explores biophysical properties of chromosomes and other cellular assemblies
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2018
people-perspectivesscience
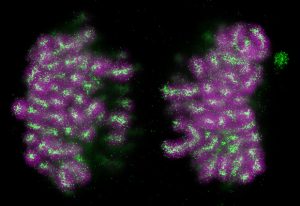
New research reveals that two different mechanisms are responsible for chromosome folding
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
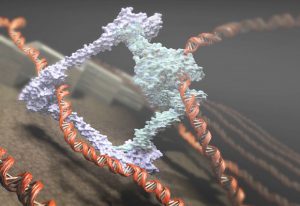
EMBL researchers and collaborators unravel how chromosomes form
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
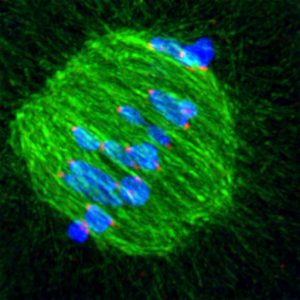
When an egg cell is being formed, the cellular machinery which separates chromosomes is extremely imprecise at fishing them out of the cell’s interior, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have discovered. The unexpected degree of trial-and-error…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
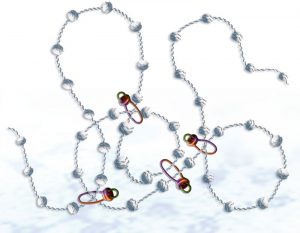
As any rock-climber knows, trailing a long length of rope behind you is not easy. A dangling length of rope is unwieldy and hard to manoeuvre, and can get tangled up or stuck on an outcropping. Cells face the same problem when dragging chromosomes apart during cell division. The chromosomes are…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have developed a new method for studying gene regulation, by employing a jumping gene as an informant. Published online today in Nature Genetics, the new method is called GROMIT. It enables researchers to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) in Hinxton, UK, have revealed new insights into how sex chromosomes are regulated. A chromatin modifying enzyme helps compensate for the fact that…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Which genes are passed on from mother to child is decided very early on during the maturation of the egg cell in the ovary. In a cell division process that is unique to egg cells, half of the chromosomes are eliminated from the egg before it is fertilised. Using a powerful microscope, researchers…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
A human cell contains an enormous 1.8 metres of DNA partitioned into 46 chromosomes. These have to be copied and distributed equally into two daughter cells at every division. Condensation, the shortening of chromosomes, allows the cell to handle such huge amounts of genetic material during cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Recent research at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) reveals new insights into how cells achieve equality between the sexes. A new link discovered between the membrane surrounding the nucleus and the male X-chromosome in fruit flies may play a crucial role in determining how active…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Microtubules need a helping hand to find chromosomes in dividing egg cells, scientists have discovered. Although it was generally accepted that microtubules act alone as the cellular ropes to pull chromosomes into place, a new study by researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL)…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
No results found