
From the bench to the EMBL Imaging Centre: when science meets art
Scientists share their experiences of creating stunning images at the EMBL Imaging Centre.
CONNECTIONS2025
connections
Showing results out of

Scientists share their experiences of creating stunning images at the EMBL Imaging Centre.
CONNECTIONS2025
connections

Imaging lets us observe biology in action – it makes visible the hidden processes of life. From its founding, EMBL has been a centre of breakthroughs and developments in bioimaging, and it continues to play a pioneering role in this field today.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
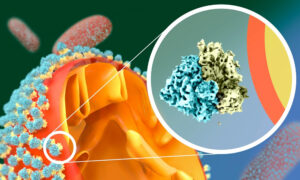
Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg and University of Virginia revealed a new cellular response to starvation: ribosomes attach to the mitochondrial outer membrane in a very unusual way, via their small subunit. The finding made in yeast might provide insights into how cancer cells survive the harsh…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
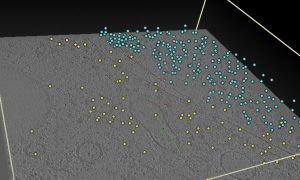
Data obtained through cryogenic sample electron tomography (cryo-ET) are openly available in the new Electron Microscopy Public Image Archive (EMPIAR) cryo-ET tomography browser.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2024
announcementsembl-announcements

Home to some of Europe’s most cutting-edge tools in molecular biology, EMBL has long shared its expertise and access to these tools through an extensive repertoire of courses, conferences, seminars, and other training. And now included in this mix is a job shadowing programme at EMBL Imaging…
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-mattersscience-technology

Together with his team, Gergely Papp pushes the frontiers of technology development in the field of structural biology.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2023
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
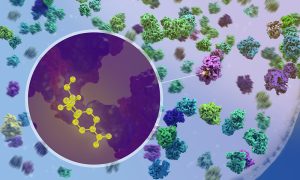
New research by EMBL scientists shows at atomic detail how antibiotics affect the process of protein production inside bacteria.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
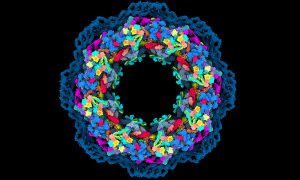
Scientists have solved several mysteries around the structure and function of a true molecular giant: the human nuclear pore complex. They created the most complete model of the complex thanks to combining the program AlphaFold2 with cryo-electron tomography, integrative modelling, molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
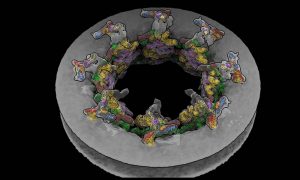
EMBL Hamburg’s Kosinski Group, the Beck Laboratory at the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics, and colleagues at EMBL Heidelberg recorded the nuclear pore complex contracting in living cells. They visualised the movement with an unprecedented level of detail with help of new software called…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Correlative microscopy service enables PhD student from Switzerland to study structure and location of proteins cells use to communicate.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
lab-mattersscience-technology
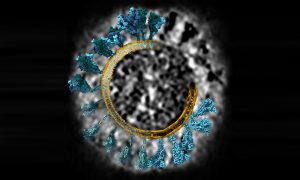
What does coronavirus’s spike protein look like in 3D? EMBL scientists and colleagues used cryo-electron tomography and molecular dynamics simulations to find out.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
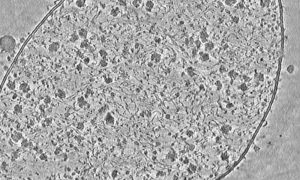
Liang Xue used cryo-electron tomography to capture this detailed image of a Mycoplasma pneumoniae cell.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

While cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) was first envisioned in 1968, the advances the Mahamid group are bringing to this 3D method for studying molecules directly inside cells are new, and are likely to greatly expand its use.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
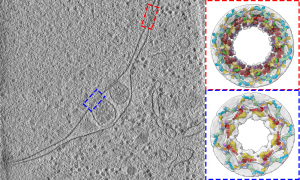
Scientists from the Beck group have studied the 3D structure of nuclear pores in budding yeast. They show how the architecture of the nuclear pore complex differs inside cells compared to its form observed in vitro studies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
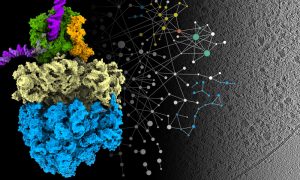
A new approach that allows researchers to see molecular machinery at work inside cells has offered a deeper understanding of how bacteria produce proteins and a unique glimpse into how they respond to antibiotics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL Heidelberg reopens the Cryo-Electron Microscopy Service Platform to support coronavirus structural biology research.
CONNECTIONS2020
connectionsscience
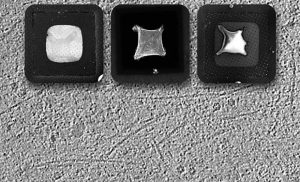
A new technique in cryo-EM
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
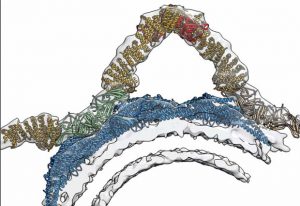
Retromer’s 3D structure improves understanding of cellular sorting and packaging
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
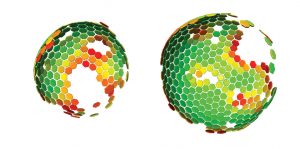
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the University Clinic Heidelberg, Germany, have produced a three-dimensional reconstruction of HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus), which shows the structure of the immature form of the virus at unprecedented detail. Immature HIV is…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
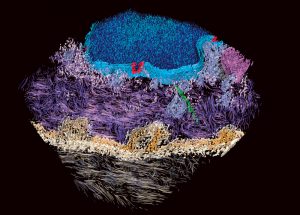
Seeing proteins in their natural environment and interactions inside cells has been a longstanding goal. Using an advanced microscopy technique called cryo-electron tomography, researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have visualised proteins responsible for cell-cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
No results found