15 November 2023

Promiscuity is critical for nourishment. How? This question lies at the focus of research by the Löw Group at EMBL Hamburg. Using structural biology methods, they explore how specialised molecules located in the cell membrane allow cells absorb nutrients from their environment.
EMBLetc
17 October 2023
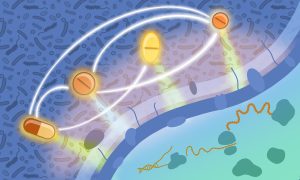
In an extensive investigation, EMBL researchers have tested over 10,000 drug combinations against some of the leading pathogenic bacteria carrying antimicrobial resistance and causing mortality.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
26 September 2022

Researchers have come up with a way to test the efficacy of hundreds of anticancer drug combinations – simultaneously, rapidly, and accurately.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
8 December 2021
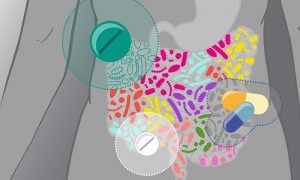
Researchers studying a massive cohort of European patients have found that commonly prescribed drugs for cardiometabolic disorders can have long-term effects on the gut microbiome. Such effects can complicate the understanding of how disease affects the microbiome and must be taken into…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
3 November 2021
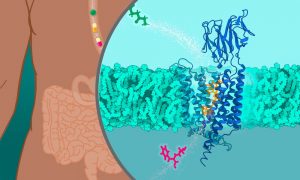
Scientists at EMBL Hamburg determined the molecular structure of Peptide Transporters 1 and 2. The findings will enable developing drugs that more efficiently pass from the gut to target tissues.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
8 September 2021
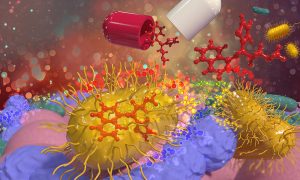
A new collaborative study led by EMBL group leaders Kiran Patil, Nassos Typas, and Peer Bork has found that common medications accumulate in human gut bacteria. This process reduces drug effectiveness and affects the metabolism of common gut microbes, thereby altering the gut microbiome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
9 February 2021

Researchers at EMBL Heidelberg have identified sequences in human proteins that might be used by SARS-CoV-2 to infect cells. They have discovered that the virus might hijack certain cellular processes, and they discuss potentially relevant drugs for treating COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
29 September 2020

To study the effect of commonly used drugs on bacterial envelopes, EMBL scientists applied a biochemical assay using a colour reaction. The deeper the red, the stronger the disruptive effect of the drug.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
8 September 2020
Researchers have found the cause of dilated cardiomyopathy – a leading cause of heart failure – and identified a potential treatment for it: a drug already used to treat acne.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
1 July 2020

Open Targets welcomes new Informatics Science Director
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2020
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
15 April 2020

EMBL researchers are studying how drugs that have shown good results against COVID-19 work in living cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
22 January 2020

The new EMBL spinoff company Araxa Biosciences GmbH aims to set new standards for the development of antibody-based therapeutics and diagnostics
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
lab-mattersscience-technology
20 January 2020
EMBL scientists identify drug targets in blood and organs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
3 June 2019
Snapshots of the flu virus replication machine in action
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
11 March 2019

Scientists develop technology to measure how ATP concentration affects protein solubility in cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
23 January 2019

New director drives drug discovery partnership forward
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2019
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
6 July 2018

EMBL scientists investigate how bacteria melt to study their reaction to drugs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
4 July 2018
Combining antibiotics with each other, non-antibiotic drugs or food additives can alter their effectiveness
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
22 June 2018

Combinations of cancer drugs can be quickly and cheaply tested using a novel microfluidic device
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
19 March 2018
One in four drugs with human targets inhibit the growth of bacteria in the human gut, and may promote antibiotic resistance, EMBL researchers report in Nature
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
11 August 2013
Like a fireman who becomes an arsonist, a protein that prevents cells becoming cancerous can also cause tumours, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have discovered. The finding, published today in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, stems…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
21 June 2012
Savira pharmaceuticals GmbH, a spin-off of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) based in Vienna, Austria, has signed a collaboration and license agreement with Roche, thus further strengthening the links between fundamental research and major pharmaceutical development companies. This…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
11 July 2008
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) discovered a new way to make use of drugs’ unwanted side effects. They developed a computational method that compares how similar the side effects of different drugs are and predicts how likely the drugs act on the same target…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
11 February 2007
We all know that iron deficiencies are dangerous, but also too much iron is bad for our health. Our body stores excess iron in various tissues, where it can lead to organ failure and even death if not treated before irreversible damage has occurred. Researchers from the Innsbruck Medical…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
No results found




















