
Cute molecules and the scientists who adore them: Sofia Rucli
Sofia Rucli, postdoc at EMBL Rome, talks about her relationship with the protein OGT, a molecular ‘candy man’ of the cell.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2024
people-perspectives
Showing results out of

Sofia Rucli, postdoc at EMBL Rome, talks about her relationship with the protein OGT, a molecular ‘candy man’ of the cell.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2024
people-perspectives

EMBL Grenoble’s Kowalinski Group analysed the structure of an enzyme responsible for modifying tRNA molecules to fine-tune protein production. They discovered that to distinguish almost identical, yet different, tRNA molecules, the enzyme uses help from another enzyme – a type of cooperation…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

An interdisciplinary collaboration between Hamburg scientists has yielded new insights into the structure and function of a heat-resistant enzyme from an exotic microbe. In this interview, EMBL Hamburg’s Matthias Wilmanns and TUHH’s Garo Antranikian discuss how their collaboration developed and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology
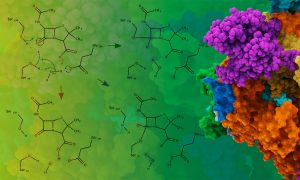
Enzymes constitute a large fraction of genomes – 20% in humans – which makes them a very important part of life. Despite decades of studies and a rich literature dedicated to understanding the reaction mechanisms of enzymes, the rules of enzyme catalysis are still not fully clear. A new…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
science-technologytechnology-and-innovation
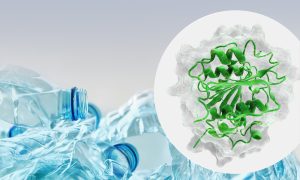
EMBL-EBI’s MGnify data resource helps researchers find enzymes for novel applications.
2022
announcementsscience
Using metagenomic data to find novel enzymes for plastic degradation and beyond
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
EMBL recognises the outstanding work of alumni with the John Kendrew and Lennart Philipson Awards
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2018
alumniembl-announcements
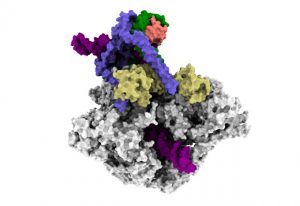
EMBL researchers uncover how a key enzyme that helps cells make new proteins starts its work
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
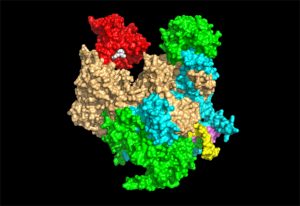
ERC grantee Stephen Cusack shares his vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
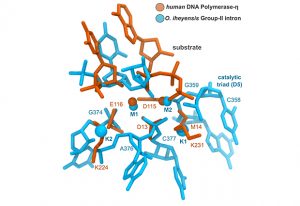
EMBL scientists superimpose structures of two-metal-ion enzymes and reveal new potential drug targets
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
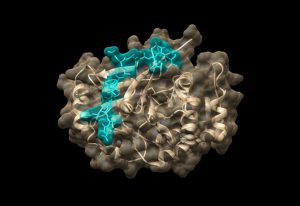
ERC grantee Maja Köhn shares her vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
Enzyme Portal makes it easier to explore all enzyme-related data in EMBL-EBI’s public resources.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
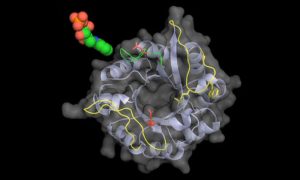
In a paper published online today in PNAS, scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Hamburg, Germany, reveal new insights into the workings of enzymes from a group of bacteria including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. The new findings…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
Our genome is constantly under attack from things like UV light and toxins, which can damage or even break DNA strands and ultimately lead to cancer and other diseases. Scientists have known for a long time that when DNA is damaged, a key enzyme sets off a cellular ‘alarm bell’ to alert the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Proteins are the executive agents that carry out all processes in a cell. Their activity is controlled and modified with the help of small chemical tags that can be dynamically added to and removed from the protein. 25 years after its first discovery, researchers at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Influenza is and remains a disease to reckon with. Seasonal epidemics around the world kill several hundred thousand people every year. In the light of looming pandemics if bird flu strains develop the ability to infect humans easily, new drugs and vaccines are desperately sought. Researchers at…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) in Hinxton, UK, have revealed new insights into how sex chromosomes are regulated. A chromatin modifying enzyme helps compensate for the fact that…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
A new mechanism to attack hard-to-treat fungal infections has been revealed by scientists from the biotech company Anacor Pharmaceuticals Inc., California, and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL] outstation in Grenoble, France. In the current issue of Science they describe…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
A human cell contains an enormous 1.8 metres of DNA partitioned into 46 chromosomes. These have to be copied and distributed equally into two daughter cells at every division. Condensation, the shortening of chromosomes, allows the cell to handle such huge amounts of genetic material during cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Living organisms need to sense the amount of energy that is available to them and regulate the activity of their genes accordingly. Scientists have made the unexpected finding that a histone protein, which wraps DNA into tight bundles and regulates gene activity, can bind a small molecule produced…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
No results found