5 March 2025

New EMBL-EBI project explores the use of a concept developed in aerospace engineering to support rare disease research, diagnosis, and treatment.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2025
people-perspectivestechnology-and-innovation
13 February 2025
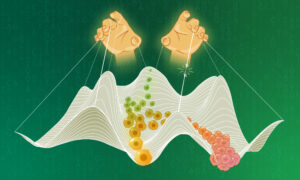
Scientists at EMBL and DKFZ have discovered how cells in the liver maintain their identity and avoid becoming tumour cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
12 February 2025

Researchers in the Galej Group at EMBL Grenoble have provided new insights into the structure of the minor spliceosome, an essential RNA-protein complex.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
11 December 2024

EMBL-EBI's new Functional Genomics Team Leader will develop standards for new data types and integrate AI into workflows.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
29 November 2024
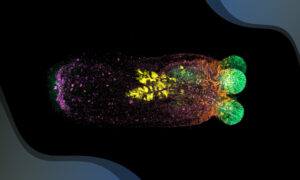
Scientists have shown how regenerating sea anemones restore their shape following a major injury, uncovering novel cellular and molecular mechanisms.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
24 September 2024

New datasets The release has 381 single-cell RNA-Seq experiments, consisting of more than 13.5 million cells from 21 different species to explore in the Single Cell Expression Atlas (SCEA). The resource now includes an entirely new class of data – externally analysed data, marked with an…
2024
updates-from-data-resources
4 September 2024

EMBL-EBI alumnus Alvis Brazma reflects on how mathematics and mountaineering have shaped his life and why keeping things simple in bioinformatics is key.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2024
people-perspectivesperspectives
2 July 2024
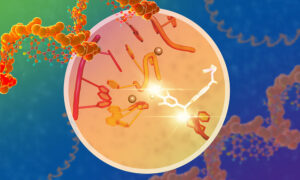
A new research paper published in Nature Communications lays the groundwork for the development of new drugs specific to genetic mutations or alterations responsible for the onset of tumours or genetic diseases.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
17 May 2024

The latest Expression Atlas 40 release is now live, containing new RNA-seq datasets, including a featured experiment resulting from a collaboration with Genotype Tissue Expression (GTEx) project as well as new proteomics data derived from our collaboration with PRIDE. In total, this release…
2024
updates-from-data-resources
4 April 2024

New study from the Galej group provides deeper structural insight into the assembly of a critical molecular machine, that removes non-coding information from genes during their expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
11 March 2024

New research from EMBL Heidelberg shows how cells in developing embryos undergo a major shift in the way they regulate gene expression as they mature and differentiate.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
sciencescience-technology
23 November 2023

Alba Diz-Muñoz and Arnaud Krebs from EMBL Heidelberg have received grants to work on projects that aim, respectively, to understand the cellular mechanics that control cell division and investigate the regulatory networks that govern transcription factor function.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS
2023
embl-announcementslab-matters
24 July 2023
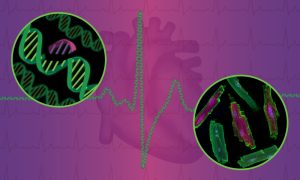
EMBL researchers have made new strides into understanding and reversing genetic defects that underlie familial heart disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
20 July 2023

The latest Expression Atlas release is now live and contains a wider range of RNA-seq and proteomics datasets.
2023
updates-from-data-resources
14 July 2023

EMBL researchers use a new cell sorting technology to gain new insights into cellular function in health and disease, as well as for other innovative applications.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
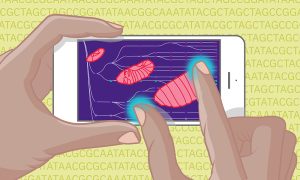
2 June 2023

A new tool for the interpretation of missense variation in humans – ProtVar – will help enable drug discovery.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation
7 February 2023
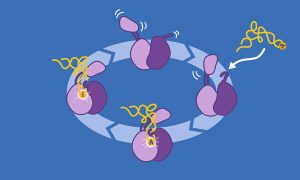
EMBL Grenoble scientists provide new insights into the function of an essential RNA editing enzyme.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2023
sciencescience-technology
19 October 2022

Data continues to be available in BioStudies.
2022
updates-from-data-resources
4 August 2022
EMBL and UW researchers plus additional collaborators have constructed a complete map of fruit fly embryonic development using machine learning. This research is foundational to better understanding overall embryo development in other species, including humans.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
4 March 2022

Genomes are made up of thousands of individual pieces – genes – which are expressed at different levels. Researchers at EMBL have shed light on how the placement of a gene affects its expression, as well as that of its neighbours.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
25 February 2022
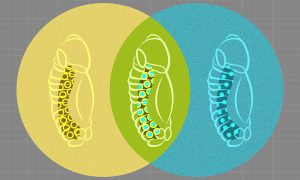
Researchers from the Furlong group at EMBL have come up with a way to observe the development of fruit-fly embryos simultaneously at the genetic and cellular levels, generating a high-resolution and integrated view of how different cell lineages form.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
24 February 2022

New Expression Atlas release features differential-proteomics and baseline-proteomics experiments in collaboration with the PRIDE team at EMBL-EBI. This also includes new baseline DIA proteomics experiments as well as new differential proteomics datasets. To improve reproducibility,…
2022
updates-from-data-resources
21 January 2022
EMBL researchers, in collaboration with BD Biosciences, have demonstrated a new technology that allows rapid image-based sorting of cells. The new technology represents a major upgrade to flow cytometry and has applications in diverse life science fields.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
18 January 2022

The Galej group at EMBL Grenoble has recently obtained high resolution snapshots of a crucial step in RNA splicing involving the U2 snRNP complex, a crucial component of the human spliceosome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
16 November 2021

How genomics, open data, and multidisciplinary science can improve food security.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
5 October 2021

EMBL scientists and colleagues have developed an interactive atlas of the entire marine worm Platynereis dumerilii in its larval stage. The PlatyBrowser resource combines high-resolution gene expression data with volume electron microscopy images.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
4 March 2021
Scientists in the Stegle group and colleagues have studied induced pluripotent stem cells from around 1,000 donors to identify correlations between individual genetic variants and altered gene expression. They linked more than 4,000 of the genetic variants responsible for altered expression…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
5 February 2021
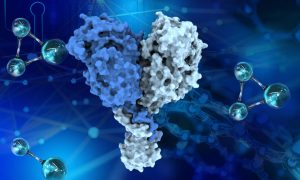
A new paper from the Galej group at EMBL Grenoble describes the structure of key parts of the Integrator complex, involved in gene expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
19 August 2020
Discoveries at EMBL will help researchers to interpret one of the most common types of experiments in genomics and medical studies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
14 July 2020
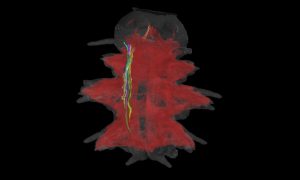
The image shows a larva of Platynereis dumerilii, a marine worm. The image here was produced by Constantin Pape, a visiting predoctoral fellow in the Kreshuk group at EMBL Heidelberg.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
1 June 2020
Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg have developed a new method, called Targeted Perturb-seq (TAP-seq), which increases the scale and precision of functional genomics CRISPR–Cas9 screens by orders of magnitude. Their method overcomes limitations in previous applications of single-cell RNA sequencing,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
9 April 2020
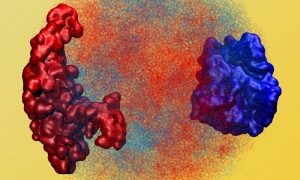
EMBL researchers in the Heard group at EMBL Heidelberg explore the interaction between DNA organisation and gene expression in the early embryo
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
3 April 2020
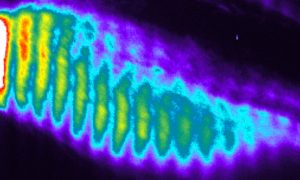
EMBL scientists examine the molecular causes of a rare hereditary disease of the spine and ribs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
5 March 2020
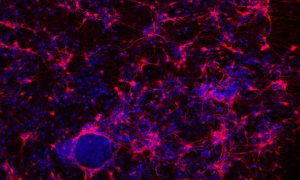
EMBL researchers investigate the role of a histone protein in regulating gene expression
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
24 July 2019
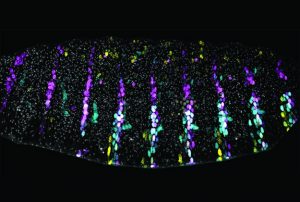
Enhancers in Drosophila embryos gather together to preserve phenotypes under stressful conditions
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
15 July 2019

Does rearranging chromosomes affect their function? EMBL scientists reveal uncoupling of 3D chromatin organisation and gene expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
28 May 2018
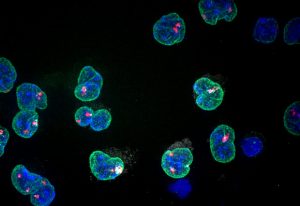
EMBL’s next Director General reflects on the questions that drive her research
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
9 February 2018

EMBL’s new group leader studies how gene expression is controlled
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
30 January 2018
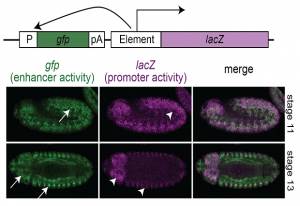
EMBL scientists show that some promoters can act as enhancers and vice versa
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
29 June 2017
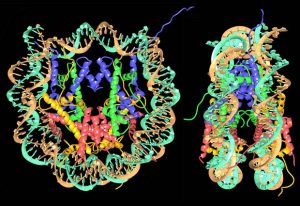
Tim Richmond looks back on the work that revealed the high-resolution structure of the nucleosome
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
eventsscience-technology
9 June 2017
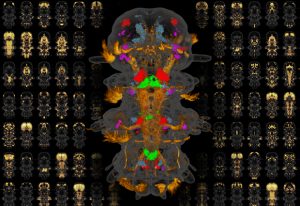
EMBL researchers complete a molecular atlas showing gene expression in all cells in an entire animal
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
6 June 2017
Two EMBL researchers are exploring new ways to filter out noise and get to the data they need
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
13 March 2017
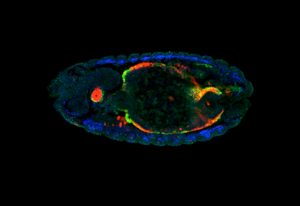
ERC grantee Eileen Furlong shares her vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
26 January 2017

Healing and anxiety are influenced by the genetics of one’s social partners
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
25 January 2017

New group leader Wojciech Galej investigates RNA-protein complexes involved in gene expression
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
24 November 2016

EMBL alumnus Jop Kind reflects on the questions that led him to this year’s John Kendrew Award
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2016
alumnipeople-perspectives
9 November 2015
Embryology, genomics and bioinformatics combine to identify factors regulating mammalian pluripotency.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
14 October 2015

Study of mouse embryonic stem cells reveals new genes involved in the stem-cell regulatory network.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
14 April 2015
New single-cell genomics techniques bring ‘omics to evolution and development research.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
8 January 2012
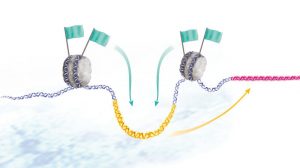
As an embryo develops, different genes are turned on in different cells, to form muscles, neurons and other bodily parts. Inside each cell’s nucleus, genetic sequences known as enhancers act like remote controls, switching genes on and off. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
4 November 2009
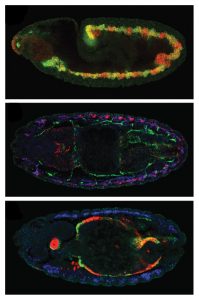
Embryonic development is like a well-organised building project, with the embryo’s DNA serving as the blueprint from which all construction details are derived. Cells carry out different functions according to a developmental plan, by expressing, i.e. turning on, different combinations of genes.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
28 May 2009
Proteins are the executive agents that carry out all processes in a cell. Their activity is controlled and modified with the help of small chemical tags that can be dynamically added to and removed from the protein. 25 years after its first discovery, researchers at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
6 March 2008
Epigenetic regulation – modifications to the structure of chromatin that influence which genes are expressed in a cell – is a key player in embryonic development and cancer formation. Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg now gained new insight…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
No results found
















































