19 June 2024
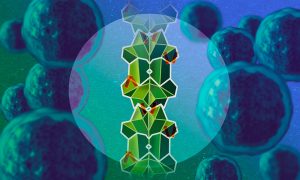
EMBL Hamburg scientists and collaborators discovered a new molecular mechanism in which an unstructured protein disables one of the main cancer-promoting proteins by gluing them into an elongated stack. Data from human patient samples support the role of this mechanism in prostate cancer…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
9 May 2024

A study from the Hackett group at EMBL Rome led to the development of an epigenetic editing system that allows to precisely program chromatin modifications at any specific position in the genome, to understand their causal role in transcription regulation.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
11 March 2024

New research from EMBL Heidelberg shows how cells in developing embryos undergo a major shift in the way they regulate gene expression as they mature and differentiate.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2024
sciencescience-technology
4 August 2022
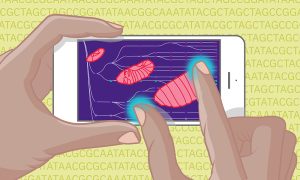
EMBL and UW researchers plus additional collaborators have constructed a complete map of fruit fly embryonic development using machine learning. This research is foundational to better understanding overall embryo development in other species, including humans.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
25 February 2022
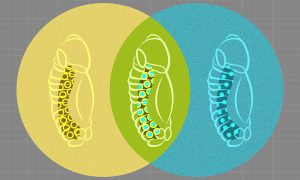
Researchers from the Furlong group at EMBL have come up with a way to observe the development of fruit-fly embryos simultaneously at the genetic and cellular levels, generating a high-resolution and integrated view of how different cell lineages form.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
23 February 2022

Michael Dorrity, one of EMBL’s newest group leaders, is studying how the environment influences early life stages in zebrafish.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2022
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
5 February 2021
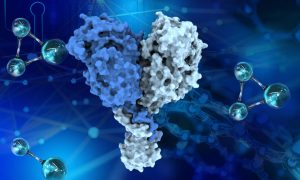
A new paper from the Galej group at EMBL Grenoble describes the structure of key parts of the Integrator complex, involved in gene expression.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
19 August 2020
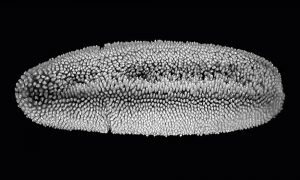
Discoveries at EMBL will help researchers to interpret one of the most common types of experiments in genomics and medical studies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
3 April 2020
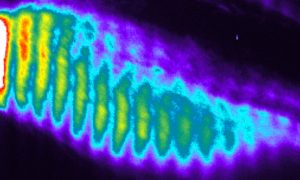
EMBL scientists examine the molecular causes of a rare hereditary disease of the spine and ribs
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
5 March 2020
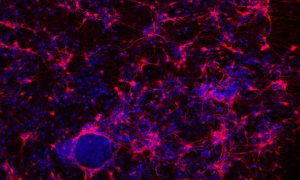
EMBL researchers investigate the role of a histone protein in regulating gene expression
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
28 May 2018
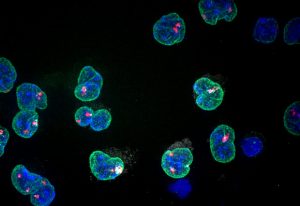
EMBL’s next Director General reflects on the questions that drive her research
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2018
people-perspectivesscience
20 March 2018
EMBL scientists discover how blood vessel cells become blood stem cells during embryonic development
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
14 March 2018
EMBL scientists show how chromatin usage in individual cells reveals developmental trajectories
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
12 February 2018
Network of genes linked to development of diabetes
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
30 January 2018
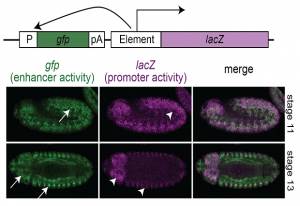
EMBL scientists show that some promoters can act as enhancers and vice versa
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2018
sciencescience-technology
28 December 2017

EMBL scientists unveil how 3D chromatin structure affects RNA splicing
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
4 December 2017

New group leader based in Grenoble aims to unveil the mechanisms of RNA editing
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
30 November 2017

James Sharpe, Head of EMBL Barcelona, co-chairs the morphogenetic engineering-themed conference
CONNECTIONS
11 August 2017

Meet Justin Crocker, EMBL’s new group leader in gene regulation during evolution and development
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2017
people-perspectivesscience
29 June 2017
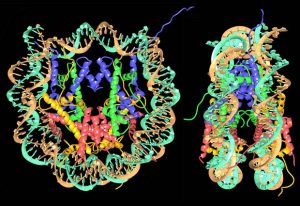
Tim Richmond looks back on the work that revealed the high-resolution structure of the nucleosome
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
eventsscience-technology
13 April 2017
EMBL-EBI researchers identify mouse epigenetic clock that could help scientists understand ageing
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
13 March 2017
ERC grantee Eileen Furlong shares her vision for the next ten years
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
12 January 2017

New mechanism revealed
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
17 May 2016

From shared interests at a conference to a surprising discovery
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
16 February 2016
How stem cells resist change
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
3 August 2015
How T-cells are trained on what not to kill
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
9 July 2015
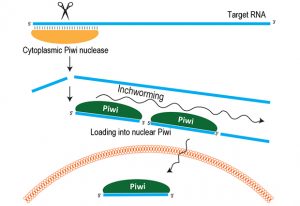
European team identify mechanism for producing piRNAs that silence jumping genes in germline cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
28 January 2015

New Bar-ChIP method makes it easier to search for epigenetic marks in many samples at once
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
27 January 2015
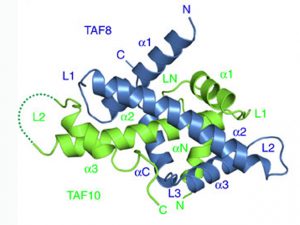
First experimental proof that a key cellular machine forms by uniting pre-assembled modules.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2015
sciencescience-technology
18 November 2014

The important thing is forming good biological questions, says new group leader in Genome Biology.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2014
people-perspectivesscience
14 October 2014

Experts from multiple fields come together to understand how the instructions in genes are read
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
eventsscience-technology
10 October 2014

From vitamin C to safe matches, a sample of notable scientists from our newest prospect member state.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
2014
people-perspectivesscience
20 August 2014
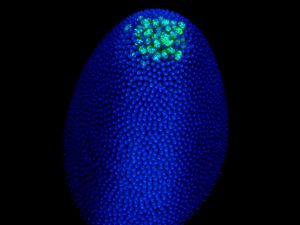
Vasa protein preserves pieces of 'enemy' DNA to help protect the genes of future generations.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
2 July 2014

Surprising finding: enhancers find their targets long before activation in Drosophila embryos
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
25 June 2014
Scientists determine the structure of auxin response factors: daisy-chains that regulate gene expression
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
25 June 2014

Enabling neighbours: intact genes can cause cancer when placed near "enhancing" regions of DNA
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
25 May 2014
How a DNA stretch influences face formation and contributes to common congenital malformations
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2014
sciencescience-technology
28 February 2013
During embryo development, genes are dynamically, and very precisely, switched on and off to confer different properties to different cells and build a well-proportioned and healthy animal. Fgf8 is one of the key genes in this process, controlling in particular the growth of the limbs and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
8 January 2012
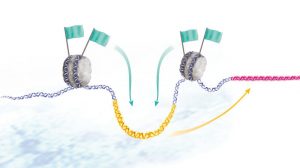
As an embryo develops, different genes are turned on in different cells, to form muscles, neurons and other bodily parts. Inside each cell’s nucleus, genetic sequences known as enhancers act like remote controls, switching genes on and off. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2012
sciencescience-technology
20 March 2011
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have developed a new method for studying gene regulation, by employing a jumping gene as an informant. Published online today in Nature Genetics, the new method is called GROMIT. It enables researchers to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
3 February 2011
In our not-so-distant evolutionary past, stress often meant imminent danger, and the risk of blood loss, so part of our body’s stress response is to stock-pile blood-clotting factors. Scientists in the Molecular Medicine Partnership Unit (MMPU), a collaboration between the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
24 June 2010
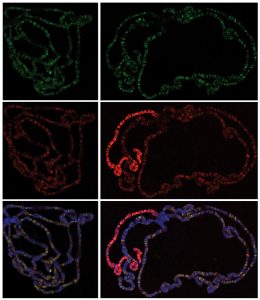
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and the Max-Planck Institute of Immunobiology Freiburg have identified a novel protein complex that regulates around 4000 genes in the fruit fly Drosophila and likely plays an important role in mammals, too.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
18 March 2010
Once the human genome was sequenced in 2001, the hunt was on for the genes that make each of us unique. But scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and Yale and Stanford Universities in the USA, have found that we differ from each other mainly because…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
16 March 2006
Recent research at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) reveals new insights into how cells achieve equality between the sexes. A new link discovered between the membrane surrounding the nucleus and the male X-chromosome in fruit flies may play a crucial role in determining how active…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
19 June 2005
Living organisms need to sense the amount of energy that is available to them and regulate the activity of their genes accordingly. Scientists have made the unexpected finding that a histone protein, which wraps DNA into tight bundles and regulates gene activity, can bind a small molecule produced…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2005
sciencescience-technology
No results found



































