Gut microbes implicated in bladder cancer
Study shows that gut bacteria can metabolise carcinogens and cause them to accumulate in distant organs, leading to tumour development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
Showing results out of

Study shows that gut bacteria can metabolise carcinogens and cause them to accumulate in distant organs, leading to tumour development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
Scientists from EMBL Rome and EMBL Heidelberg found that disrupting the gut microbiome of male mice increases the risk of disease in their offspring. Their findings suggest that a father’s pre-conception environment can have lifelong effects on offspring.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

Promiscuity is critical for nourishment. How? This question lies at the focus of research by the Löw Group at EMBL Hamburg. Using structural biology methods, they explore how specialised molecules located in the cell membrane allow cells absorb nutrients from their environment.
EMBLetc2023
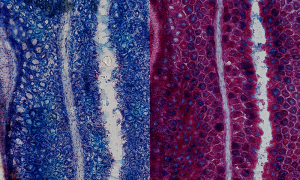
Mucus present in the mouse colon can be visualised using Alcian blue staining, as imaged here by EMBL predoctoral fellow Linda Decker.
LAB MATTERSSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
lab-matterspicture-of-the-weekscience-technology

EMBL researchers used data from over 300 human faecal microbiota transplants to gain an ecological understanding of what happens when two gut microbiomes clash.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
Researchers studying a massive cohort of European patients have found that commonly prescribed drugs for cardiometabolic disorders can have long-term effects on the gut microbiome. Such effects can complicate the understanding of how disease affects the microbiome and must be taken into…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Maria Zimmermann-Kogadeeva is one of EMBL’s newest group leaders and a computational biologist whose research group applies computational modelling to better understand the metabolism of gut bacteria and their potential to have far-reaching impacts on other organs.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
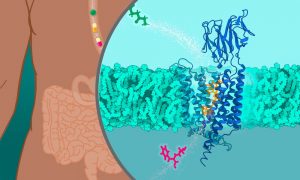
Scientists at EMBL Hamburg determined the molecular structure of Peptide Transporters 1 and 2. The findings will enable developing drugs that more efficiently pass from the gut to target tissues.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from EMBL’s Typas group and collaborators have analysed the effects of 144 antibiotics on the wellbeing of gut microbes. The study improves our understanding of antibiotics’ side effects and suggests a new approach to mitigating the adverse effects of antibiotics therapy on gut…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

In the lab, Diënty Hazenbrink works with microbes that live in our guts. In her free time, she enjoys wildlife photography. A shared set of skills facilitates both activities.
LAB MATTERSPEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2021
lab-matterspeople-perspectives
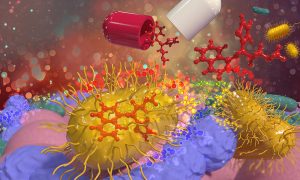
A new collaborative study led by EMBL group leaders Kiran Patil, Nassos Typas, and Peer Bork has found that common medications accumulate in human gut bacteria. This process reduces drug effectiveness and affects the metabolism of common gut microbes, thereby altering the gut microbiome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Researchers investigate how external factors can influence the persistence of microbe species in the human gut
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
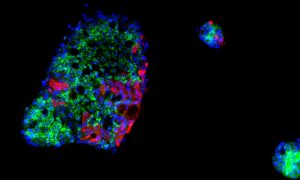
EMBL scientists, together with collaborators from Heidelberg University, have provided further evidence of the gut’s role in COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Scientists identify more than 140 000 virus species in the human gut; more than half have never been seen before
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Scientists at EMBL and Heidelberg University Hospital are studying how the novel coronavirus behaves in the gut to try to better understand its epidemiology and prevent its spread. To do this, they are combining advanced imaging and sequencing technologies to study coronavirus in human intestinal…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Colorectal cancer characterised by consistent changes in gut bacteria across continents, cultures and diets
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology
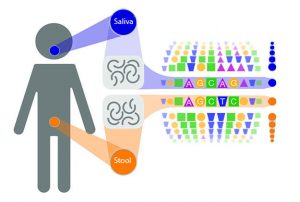
Many microbes traverse the oral-gut barrier
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

Dog and human gut microbiomes have more similar genes and responses to diet than previously thought
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2018
people-perspectivesscience
One in four drugs with human targets inhibit the growth of bacteria in the human gut, and may promote antibiotic resistance, EMBL researchers report in Nature
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists show how to grow a wide range of gut bacteria in the lab
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
In the future, when you walk into a doctor’s surgery or hospital, you could be asked not just about your allergies and blood group, but also about your gut type. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and collaborators in the international MetaHIT…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
The thousands of bacteria, fungi and other microbes that live in our gut are essential contributors to our good health. They break down toxins, manufacture some vitamins and essential amino acids, and form a barrier against invaders. A study published today in Nature shows that, at 3.3 million,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2010
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have discovered that proteins that regulate the body’s iron household play a vital role in making sure enough nutrients and water are absorbed in the intestine. Mice lacking these proteins suffer from weight loss and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
No results found