
ENA launches Data Hubs Portal
The Data Hubs Portal is a new interface that enables users to setup and manage pre-release and/or public Data Hubs at the ENA.
2025
updates-from-data-resources
Showing results out of

The Data Hubs Portal is a new interface that enables users to setup and manage pre-release and/or public Data Hubs at the ENA.
2025
updates-from-data-resources

EMBL-EBI and colleagues from other 11 institutes commit to pathogen data sharing project.
2024
announcements

The SARS-CoV-2 Data Hubs are a set of tools coupled with infrastructure that support four components: the submission, analysis, presentation and visualisation of SARS-CoV-2 raw read data, and its resulting analyses. What makes Data Hubs attractive is a unique set of features: A new publication in…
2024
updates-from-data-resources
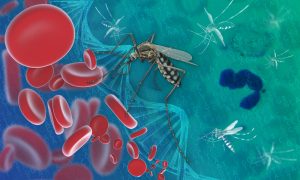
Plasmodium falciparum, a malaria parasite, uses gene conversion to produce genetic diversity in two surface protein genes targeted by the human immune system.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
announcementssciencescience-technology
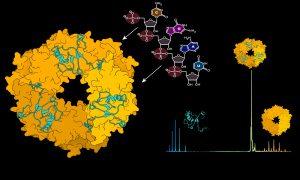
The Kosinski Group at EMBL Hamburg collaborated with other groups in Hamburg to reveal critical steps in Lassa virus ribonucleoparticle assembly and recruitment, and the crucial role played by RNA in in the Lassa virus life cycle.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

Enabling researchers worldwide to share and analyse pathogen data generated across the world
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation

The first cohort study linking data across categories was recently added on the Pathogens Portal Cohort Browser and is also accessible from the BioSamples browser. This pilot study comes from Erasmus Medical Centre through the ReCoDID project, one of the COVID-19 Data Platform supporting…
2022
updates-from-data-resources

Zamin Iqbal and his team are working with researchers all over the globe to help put a stop to Tuberculosis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology

The upcoming 22nd EMBL Science & Society Conference will explore the One Health approach, which advocates for greater cross-sectoral collaboration and communication across the human-animal-environment interface.
CONNECTIONS2021
connectionsevents

The BY-COVID project aims to make infectious disease data, including COVID-19, openly available to everyone.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
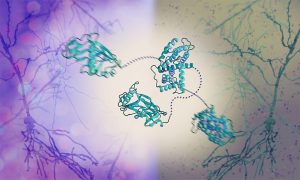
The Graham and Crump groups at the University of Cambridge and the Svergun Group at EMBL Hamburg have discovered a mechanism by which the herpes simplex virus takes control of the molecular machinery of human cells. Their work reveals how a dedicated viral protein hijacks key host proteins, forcing…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
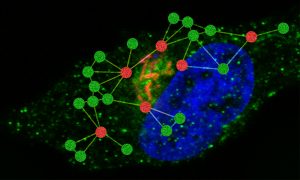
Research in the Typas group uncovers new details of the strategies Salmonella uses to survive in infected cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
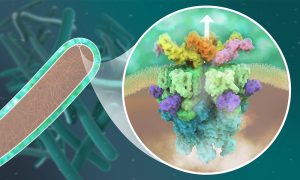
EMBL Hamburg’s Wilmanns and Kosinski groups have determined the detailed structure of a bacterial protein complex critical for tuberculosis infection.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
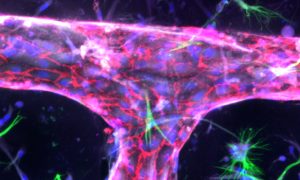
The Bernabeu Group aims to increase our knowledge of cerebral malaria, using in vitro engineered networks of human blood vessels and brain cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

EMBL scientists support research on malaria by providing freely available data resources and using innovative experimental approaches. Our Course and Conference Office facilitates the exchange of knowledge in the field by hosting the annual BioMalPar conference.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

EMBL and Portugal are bringing together leading scientists to highlight the role of fundamental research in tackling infectious diseases.
CONNECTIONS2021
connectionsevents

Researchers from EMBL and Heidelberg University Hospital combine high-resolution imaging to observe the infection process in cell nuclei, opening the door for new therapeutics.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

Freshwater sports can cause waterborne infections, but real-time DNA sequencing could help.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
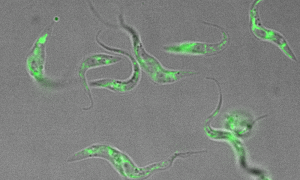
Members of the EMBL community are working to improve our understanding of the parasites that cause malaria and sleeping sickness
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
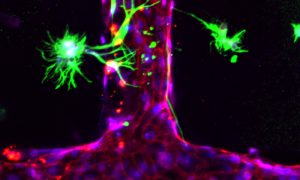
To help understand cerebral malaria the Bernabeu group has created in vitro engineered networks of human blood vessels.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
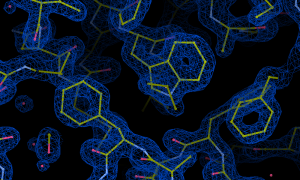
A group of scientists led by EMBL Hamburg’s Christian Löw provide insights into the molecular structure of proteins involved in the gliding movements through which the parasites causing malaria and toxoplasmosis invade human cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

European collaboration receives funding to explore risks and impact of future infectious disease outbreaks.
LAB MATTERS2020
lab-matters
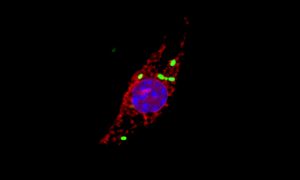
Scientists including members of EMBL’s Typas group have investigated how immune cells called macrophages respond to infection by the intracellular pathogen Salmonella enterica. They discovered that Salmonella causes newly produced cathepsins to accumulate in the nuclei of infected cells to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Scientists at EMBL Hamburg and Karolinska Institutet Stockholm aim to find synthetic antibodies – known as nanobodies – that bind a surface protein of the novel SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. Nanobodies could prevent the virus from entering human cells and causing COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

In March 2020, planes were grounded, streets went quiet, and our lives changed forever. But while the world came to a halt, many scientists were ramping up their efforts to understand the new virus.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

The new collaborative space will help scientists, public health and healthcare professionals around the world to fight the coronavirus pandemic.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

From 27–30 September, Tara will be docked in the port of Marseille, France’s second largest city.
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2019
embl-announcementsevents
Insights into the reproduction of Plasmodium parasites in mosquitoes reveal rapid and broad activity
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

Reconstructing T-cell development in high resolution
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
First detailed atlas of start points for genes expression in malaria-causing parasite
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
For many years, the mosquitoes that transmit malaria to humans were seen as public enemies, and campaigns to eradicate the disease focused on eliminating the mosquitoes. But, as a study published today in Science shows, the mosquitoes can also be our allies in the fight against this common foe,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Influenza is currently a grave concern for governments and health organisations around the world. Now one of the tactics used by influenza virus to take over the machinery of infected cells has been laid bare by structural biologists at the EMBL, the joint Unit of Virus Host-Cell Interaction of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
A new mechanism to attack hard-to-treat fungal infections has been revealed by scientists from the biotech company Anacor Pharmaceuticals Inc., California, and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL] outstation in Grenoble, France. In the current issue of Science they describe…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
In 1918, 50 million people died during a worldwide influenza pandemic caused by mutation of a bird-specific strain of the influenza virus. Recently H5N1, another highly infectious avian strain has caused outbreaks of bird flu around the world. There is great concern that this virus might also…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Liver cancer is one of the deadliest cancers worldwide; every year sees more than 400,000 new cases, and most of the victims die in less than one year. Despite extensive research, the underlying molecular mechanisms of the disease are poorly understood. A new study by researchers from the Mouse…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Today the network of excellence for Biology and Pathology of the Malaria Parasite (BioMalPar), will bring together the world’s elite in the field of Malaria research at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg. At the second annual BioMalPar conference, organised jointly…
CONNECTIONS2006
connectionsevents
Researchers at the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) in India and a unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in France have made a key discovery about a molecule that helps the malaria parasite infect human cells. India is one of the countries…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
No results found