
Thornton Building opens: a hub for collaboration and innovation
EMBl-EBI’s new building enables the translation of the institute’s data management expertise into solutions for global challenges
LAB MATTERS2025
announcementslab-matters
Showing results out of

EMBl-EBI’s new building enables the translation of the institute’s data management expertise into solutions for global challenges
LAB MATTERS2025
announcementslab-matters
Scientists at EMBL and DKFZ have discovered how cells in the liver maintain their identity and avoid becoming tumour cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2025
science-technology
EMBL scientists applied molecular engineering to build photoacoustic probes to label and visualise neurons deep within brain tissue.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology

ARISE fellow Melanie Schneider shares how she uncovered a new interest in research infrastructures and supporting discovery.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2024
people-perspectivesperspectives

Toby Gibson reflects on 38 years at EMBL, the scientific tools he built along the way, and the state of science today.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2024
people-perspectives

We are excited to announce the latest releases of IntAct and Complex Portal. IntAct 244 highlights Complex Portal 244 highlights
2023
updates-from-data-resources

InterPro version 95.0 and InterProScan 5.63-95.0 are now available! InterPro now features hundreds of new methods integrated from partner databases, and InterProScan draws on over 39000 entries. InterPro version 95.0 – new features include: InterPro 95.0 covers 81.7% of UniProt Knowledgebase…
2023
updates-from-data-resources

A new tool for the interpretation of missense variation in humans – ProtVar – will help enable drug discovery.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technologytechnology-and-innovation

InterPro 94.0 features hundreds of new methods integrated from partner databases, and InterProScan draws on over 38,000 entries.
2023
updates-from-data-resources

EMBL-EBI's metagenomics data resource increases in size and supports groundbreaking AI tools for protein structure prediction.
2023
updates-from-data-resources

InterPro now features hundreds of new methods integrated from partner databases, and InterProScan draws on over 38,000 entries. InterPro version 93.0 InterPro 93.0 integrates 300 new methods from the CDD (261), PANTHER (12), PROSITE profiles (17), SMART (9), TIGRFAMs (1) databases, and covers 81.7%…
2023
updates-from-data-resources
Researchers use social media to share findings on how useful AlphaFold predictions are for different applications.
2022
research-highlightsscience
Machine learning has helped researchers uncover new insights into how bacteria infect host cells.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology

Latest AlphaFold database update adds 27 new organisms and almost 200,000 new protein structure predictions relevant to neglected tropical diseases and antimicrobial resistance
2022
updates-from-data-resources
Researchers develop a new high-throughput approach to assess the functional significance of protein phosphosites.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
3D-Beacons Network acts as a one-stop shop for protein structures by combining and standardising data from several providers.
CONNECTIONS2021
connectionsscience
DeepMind and EMBL-EBI to make millions of protein structure predictions freely available to the scientific community.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Researchers establish a framework for identifying new drugs capable of exploiting a cell’s own machinery.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology

As perfect as a summer night sky, these nuclear pores help calibrate a customised super-resolution microscope in EMBL’s Ries group.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
EMBL scientists, together with collaborators from Heidelberg University, have provided further evidence of the gut’s role in COVID-19.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
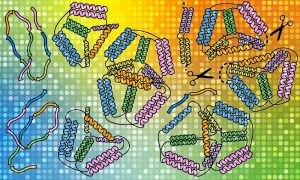
Using EMBL Hamburg’s world-class structural biology infrastructure, researchers advance the folding of protein ‘origami’ designed in the lab.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
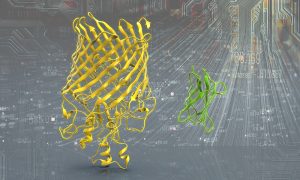
Thousands of new protein structure models, prected using deep learning, now available to explore
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
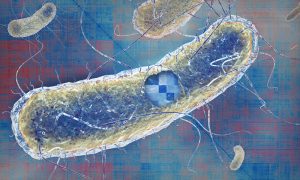
A new paper from EMBL’s Savitski team and Typas group describes their work on E. coli and how it brings a greater understanding of the way genes function and interact.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

How artificial intelligence can help us solve the mysteries of the protein universe
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
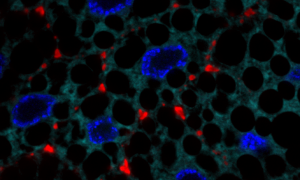
Those heart-shaped cells aren't just for show. They help tell the story of two proteins working together
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology

EMBL scientists working in the groups of Matthias Hentze and Wolfgang Huber have created RBPbase – a database of RNA-binding proteins – to assist the identification of proteins that interact with the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Schoolchildren get creative with 3D protein structures
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS2019
embl-announcementsscience

EMBL scientists collaborate to develop new protocol for screening membrane protein stability
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

EMBL scientists have discovered that the proteome is substantially affected by both sex and diet
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2019
sciencescience-technology

PDBe-KB - new data resource for protein structure and function launches
LAB MATTERS2019
lab-matters
Real-time tracking of proteins during mitosis is now possible using a 4D computer model
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, have developed a new method which enables researchers to label any protein of their choice with any of a wide variety of previously available compounds, in living cells, by introducing a single reactive…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2011
sciencescience-technology
Proteins are the executive agents that carry out all processes in a cell. Their activity is controlled and modified with the help of small chemical tags that can be dynamically added to and removed from the protein. 25 years after its first discovery, researchers at the European Molecular Biology…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have discovered that proteins that regulate the body’s iron household play a vital role in making sure enough nutrients and water are absorbed in the intestine. Mice lacking these proteins suffer from weight loss and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
Seeing proteins in their natural environment and interactions inside cells has been a longstanding goal. Using an advanced microscopy technique called cryo-electron tomography, researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) have visualised proteins responsible for cell-cell…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the Samuel Lunenfeld Research Institute of Mount Sinai Hospital (Canada), the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (Germany), and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (USA) have created a new computational method called NetworKIN. This method uses biological networks to better…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Over 30% of our genes are under the control of small molecules called microRNAs. They prevent specific genes from being turned into protein and regulate many crucial processes like cell division and development, but how they do so has remained unclear. Now researchers from the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Liver cancer is one of the deadliest cancers worldwide; every year sees more than 400,000 new cases, and most of the victims die in less than one year. Despite extensive research, the underlying molecular mechanisms of the disease are poorly understood. A new study by researchers from the Mouse…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
A cell is a busy place. In a permanent rush hour, molecules are transported along a dynamic motorway system made up of filaments called microtubules. Microtubules constantly grow and shrink and are rapidly assembled wherever a cargo needs to go, but during this transportation process they need to…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Depression, coordination and speech problems, muscle weakness and disability are just a few of the symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Researchers from the Mouse Biology Unit of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Italy and the Department of Neuropathology at the Faculty of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Ebola, measles and rabies are serious threats to public health in developing countries. Despite different symptoms all of the diseases are caused by the same class of viruses that unlike most other living beings carry their genetic information on a single RNA molecule instead of a double strand of…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
Recent research at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) reveals new insights into how cells achieve equality between the sexes. A new link discovered between the membrane surrounding the nucleus and the male X-chromosome in fruit flies may play a crucial role in determining how active…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2006
sciencescience-technology
No results found