2 December 2020
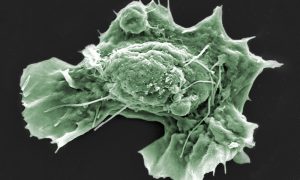
Scientists in the Diz-Muñoz group at EMBL Heidelberg are working to build understanding of the role that mechanical properties play in affecting cell behaviour – a young and rapidly developing field of study. They have developed and successfully used a highly specialised technique to manipulate…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
4 November 2019

New possibilities for gene therapies
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
24 November 2016
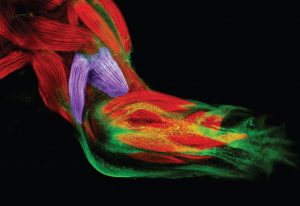
Exploring what it would take to regrow a lost limb, and what we might learn along the way
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
4 February 2013
Mature cells can be reprogrammed to pluripotency and thus regain the ability to divide and differentiate into specialized cell types. Although these so-called induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) represent a milestone in stem cell research, many of the biochemical processes that underlie…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2013
sciencescience-technology
17 December 2007
It does not take much to injure a muscle. Sometimes one sudden, inconsiderate movement does the job. Unfortunately, damaged muscles are not as efficient at repair as other tissues such as bone. Researchers of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s Mouse Biology Unit (EMBL), Italy, and…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
2 November 2006

Muscle wasting can occur at all ages as the result of genetic defects, heart failure, spinal injury or cancer. A therapy to cure the loss of muscle mass and strength, which has a severe impact on patients’ lives, is desperately sought. Blocking a central signal molecule, researchers from the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology



