The new heroics of RNA in cell differentiation
EMBL research with Enolase 1 (ENO1) points to a possible new way to understand RNA’s leading role in how cells develop.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
Showing results out of

EMBL research with Enolase 1 (ENO1) points to a possible new way to understand RNA’s leading role in how cells develop.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology

Judith Zaugg, Group Leader at EMBL Heidelberg, has been awarded an ERC Consolidator Grant of €2 million funded under the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme. Over the next five years, the grant will enable her group to study cellular interactions in the human bone…
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTSLAB MATTERS2022
embl-announcementslab-matters

A community of scientists is looking at the estimated three billion heart muscle cells in a human heart to better understand heart disease.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
alumniscience-technology
Scientists in the Stegle group and colleagues have studied induced pluripotent stem cells from around 1,000 donors to identify correlations between individual genetic variants and altered gene expression. They linked more than 4,000 of the genetic variants responsible for altered expression…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2021
sciencescience-technology
Scientists in the Diz-Muñoz group at EMBL Heidelberg are working to build understanding of the role that mechanical properties play in affecting cell behaviour – a young and rapidly developing field of study. They have developed and successfully used a highly specialised technique to manipulate…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg have investigated stem cells and how they differentiate to become neurons. Their approach included an assessment of the complex interplay of molecules during the differentiation process and generated fundamental new insights into the role of a protein called Sox2 in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
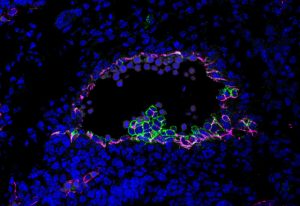
Morgan Oatley and her colleagues in Christophe Lancrin’s group investigated how haematopoietic stem cells emerge from the endothelium in developing mouse embryos.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
picture-of-the-weekscience-technology
How embryonic stem cells develop into the germ line
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology

Researchers from EMBL and Heidelberg University unveil the molecular mechanisms of ageing
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
Introducing one of the largest collections of high-quality human induced pluripotent stem cells
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology
Study by EMBL and DKFZ researchers means origins of myeloid leukaemias may need rethinking
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2017
sciencescience-technology

EMBL alumnus Jop Kind reflects on the questions that led him to this year’s John Kendrew Award
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES2016
alumnipeople-perspectives

EMBL and the Hubrecht Institute signed a 5-year partnership agreement
CONNECTIONSLAB MATTERS2016
connectionslab-matters
How stem cells resist change
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2016
sciencescience-technology
Embryology, genomics and bioinformatics combine to identify factors regulating mammalian pluripotency.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology

Study of mouse embryonic stem cells reveals new genes involved in the stem-cell regulatory network.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2015
sciencescience-technology
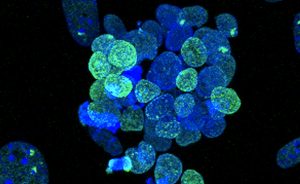
Researchers produce pristine stem cells, which can be precisely changed into clinically relevant cell types.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2014
sciencescience-technology
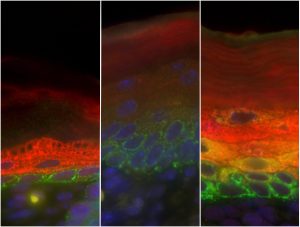
Stem cells have a unique ability: when they divide, they can either give rise to more stem cells, or to a variety of specialised cell types. In both mice and humans, a layer of cells at the base of the skin contains stem cells that can develop into the specialised cells in the layers above.…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2009
sciencescience-technology
Leukaemia – cancer of blood or bone marrow – is caused by mutations that allow defective blood cells to accumulate and displace healthy blood. To devise effective therapies it is crucial to know which mutations cause leukaemia and which cell type gives rise to leukaemic cells. Researchers from…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2008
sciencescience-technology
When a cell divides, normally the result is two identical daughter cells. In some cases however, cell division leads to two cells with different properties. This is called asymmetric cell division and plays an important role in embryonic development and the self-renewal of stem cells. Researchers…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and the Institute of Biomedical Research of the Parc Científic de Barcelona (IRB-PCB) have now added key evidence to claims that some types of cancer originate with defects in stem cells. The study, reported this week in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
No results found