11 August 2022
International consortium analyses the genetic sequences and antibiotic susceptibility of 10,000 global Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
research-highlightssciencescience-technology
23 March 2022

Zamin Iqbal and his team are working with researchers all over the globe to help put a stop to Tuberculosis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
perspectivessciencescience-technology
19 October 2021

Profiling M. tuberculosis strains from 27 countries to reveal causes of drug resistance.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
25 June 2021
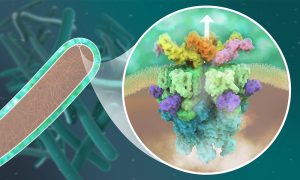
EMBL Hamburg’s Wilmanns and Kosinski groups have determined the detailed structure of a bacterial protein complex critical for tuberculosis infection.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
18 October 2019
Funding awarded to EMBL-EBI for tuberculosis monitoring tool
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
17 June 2019

EMBL Hamburg and Tara raise awareness of the risks of microplastic pollution and global infection
EMBL ANNOUNCEMENTS
2019
embl-announcementsevents
18 February 2019
Suicide system in tuberculosis bacteria might hold key to treatment
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
11 April 2017
EMBL scientists add crucial knowledge to understanding of the bacterium that causes tuberculosis
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2017
sciencescience-technology
24 March 2016
How an EMBL team is making and sharing tools to explore tuberculosis protein structures
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2016
sciencescience-technology
14 February 2011
In a paper published online today in PNAS, scientists from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Hamburg, Germany, reveal new insights into the workings of enzymes from a group of bacteria including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. The new findings…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
29 May 2006
Tuberculosis remains one of the deadliest threats to public health. Every year two million people die of the disease, which is caused by the microorganism Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Roughly one third of the world’s population is infected and more and more bacterial strains have developed…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology







