
Follow the cellular road
An AI-enhanced advanced microscopy approach offers promise in better understanding glioblastomas, one of the deadliest brain cancers.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
Showing results out of

An AI-enhanced advanced microscopy approach offers promise in better understanding glioblastomas, one of the deadliest brain cancers.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
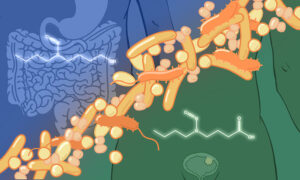
Study shows that gut bacteria can metabolise carcinogens and cause them to accumulate in distant organs, leading to tumour development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
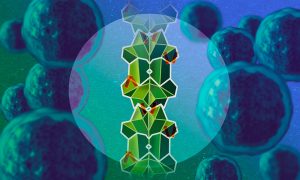
EMBL Hamburg scientists and collaborators discovered a new molecular mechanism in which an unstructured protein disables one of the main cancer-promoting proteins by gluing them into an elongated stack. Data from human patient samples support the role of this mechanism in prostate cancer…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2024
science-technology
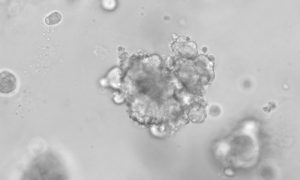
A new organoid model mimics the behaviour of neuroendocrine tumours (NETs), providing a novel and invaluable tool to study the disease in the lab.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2023
sciencescience-technology

Researchers have come up with a way to test the efficacy of hundreds of anticancer drug combinations – simultaneously, rapidly, and accurately.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2022
sciencescience-technology
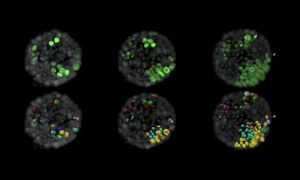
EMBL scientists have created a new, realistic 3D testbed that could help achieve the goal of stopping cancers before they start by studying cancer cells as they first form.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

EMBL co-leads most comprehensive study of genetic causes of cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
The largest and most comprehensive catalogue of cancer-specific RNA alterations reveals new insights into the cancer genome.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Researchers at EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and the Francis Crick Institute have analysed the whole genomes of over 2600 tumours from 38 different cancer types to determine the chronology of genomic changes during cancer development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Using the dataset from the Pan-Cancer project, scientists has developed methods to group, classify, and describe large rearrangements of the genome that are a key driver of cancer.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Analysis of whole cancer genomes gives key insights into the role of the non-coding genome in cancer
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology
Researchers at Harvard Medical School and EMBL-EBI have carried out the largest analysis across cancer types of the newly discovered mutational phenomenon chromothripsis.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Using the data from the Pan-Cancer project EMBL scientists describe how our genetic background influences cancer development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2020
sciencescience-technology

Combinations of cancer drugs can be quickly and cheaply tested using a novel microfluidic device
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2018
sciencescience-technology
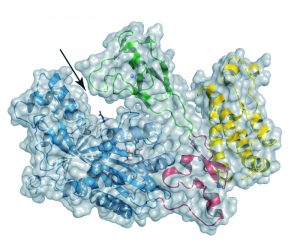
Like a fireman who becomes an arsonist, a protein that prevents cells becoming cancerous can also cause tumours, scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, have discovered. The finding, published today in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, stems…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology
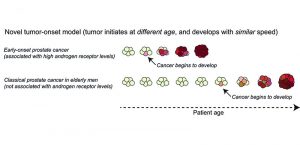
While prostate cancer is the most common cancer in elderly Western men it also, but more rarely, strikes patients aged between 35 and 50. Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, in collaboration with several other research teams in Germany*, have…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2013
sciencescience-technology

Just as banks store away only the most valuable possessions in the most secure safes, cells prioritise which genes they guard most closely, researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) have found. The study, published online today…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2012
sciencescience-technology
Liver cancer is one of the deadliest cancers worldwide; every year sees more than 400,000 new cases, and most of the victims die in less than one year. Despite extensive research, the underlying molecular mechanisms of the disease are poorly understood. A new study by researchers from the Mouse…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2007
sciencescience-technology
Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and the Institute of Biomedical Research of the Parc Científic de Barcelona (IRB-PCB) have now added key evidence to claims that some types of cancer originate with defects in stem cells. The study, reported this week in…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY2005
sciencescience-technology
No results found