8 August 2024

EMBL-Stanford Life Science Alliance fellow Jana Helsen shares how she balanced her life between two laboratories and countries, her latest research paper, and her passion for cover art.
PEOPLE & PERSPECTIVES
4 March 2022

Genomes are made up of thousands of individual pieces – genes – which are expressed at different levels. Researchers at EMBL have shed light on how the placement of a gene affects its expression, as well as that of its neighbours.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2022
sciencescience-technology
18 October 2021
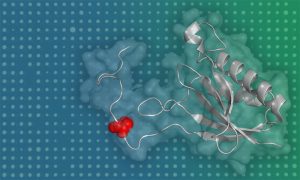
Researchers develop a new high-throughput approach to assess the functional significance of protein phosphosites.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
4 January 2021
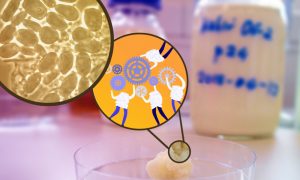
Researchers discovered the dominant species of bacteria in kefir grains cannot endure without other species that help the 'team' survive.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2021
sciencescience-technology
7 December 2020

While cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) was first envisioned in 1968, the advances the Mahamid group are bringing to this 3D method for studying molecules directly inside cells are new, and are likely to greatly expand its use.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
3 September 2020
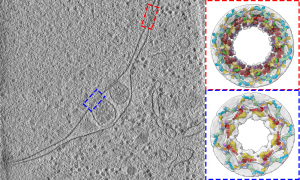
Scientists from the Beck group have studied the 3D structure of nuclear pores in budding yeast. They show how the architecture of the nuclear pore complex differs inside cells compared to its form observed in vitro studies.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2020
sciencescience-technology
4 June 2019
Most of us love brewer’s yeast, or at least the food that it’s helped us to produce since ancient times. Without Saccharomyces cerevisiae (its Latin name) we couldn’t enjoy wine, beer or most types of bread. Besides its role in food production, S. cerevisiae is also an important model…
LAB MATTERS
2019
lab-matterspicture-of-the-week
4 February 2019
Scientists develop high-throughput yeast single-cell RNA sequencing method
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2019
sciencescience-technology
17 June 2011
As any rock-climber knows, trailing a long length of rope behind you is not easy. A dangling length of rope is unwieldy and hard to manoeuvre, and can get tangled up or stuck on an outcropping. Cells face the same problem when dragging chromosomes apart during cell division. The chromosomes are…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2011
sciencescience-technology
18 March 2010
Once the human genome was sequenced in 2001, the hunt was on for the genes that make each of us unique. But scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, and Yale and Stanford Universities in the USA, have found that we differ from each other mainly because…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2010
sciencescience-technology
1 October 2009
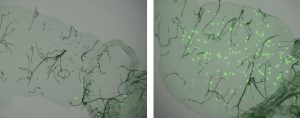
For many years, the mosquitoes that transmit malaria to humans were seen as public enemies, and campaigns to eradicate the disease focused on eliminating the mosquitoes. But, as a study published today in Science shows, the mosquitoes can also be our allies in the fight against this common foe,…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2009
sciencescience-technology
9 July 2008
Genetic recombination, the process by which sexually reproducing organisms shuffle their genetic material when producing germ cells, leads to offspring with a new genetic make-up and influences the course of evolution. In the current issue of Nature, researchers at the European Molecular…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2008
sciencescience-technology
21 October 2007
New insights into the cellular signal chain through which pheromones stimulate mating in yeast have been gained by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory [EMBL]. Similar signal chains are found in humans, where they are involved in many important processes such as the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
6 March 2007
Like our body every cell has a skeleton that provides it with a shape, confers rigidity and protects its fragile inner workings. The cytoskeleton is built of long protein filaments that assemble into networks whose overall architecture and fine detail can only be revealed with high resolution…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2007
sciencescience-technology
27 September 2006
The life of a cell is all about growing and dividing at the right time. That is why the cell cycle is one of the most tightly regulated cellular processes. A control system with several layers adjusts when key components of the cell cycle machinery are produced, activated and degraded to make sure…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
22 January 2006
Today researchers in Germany announce they have finished the first complete analysis of the “molecular machines” in one of biology’s most important model organisms: S. cerevisiae (baker’s yeast). The study from the biotechnology company Cellzome, in collaboration with the…
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
2006
sciencescience-technology
No results found










